Figure 3. Memory disruption is dependent on destabilization mediated by L-type voltage-gated Ca++ channels.
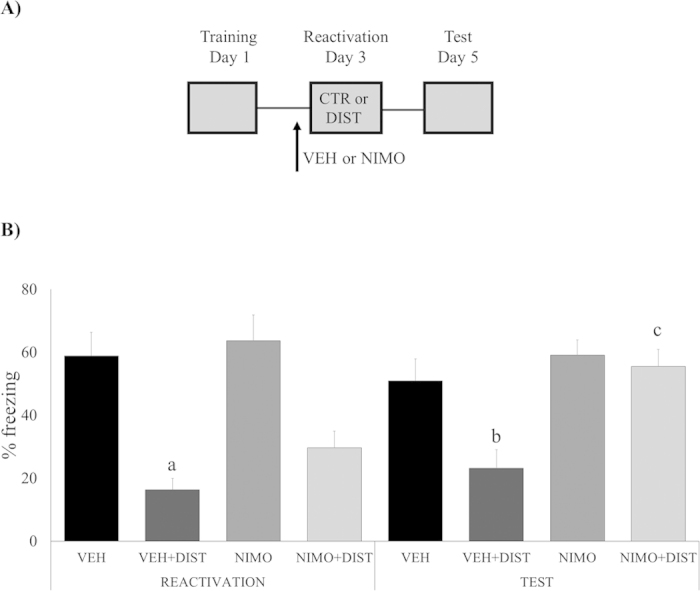
(A) Schematic representation of the behavioral procedures: 48 h after training, rats received a s.c. infusion of nimodipine (NIMO) or its vehicle (VEH), and, 30 min later, were re-exposed to the fear conditioning context without the US (shock) – the Reactivation session – either with or without the presence of a distractor (DIST); all groups were tested on day 5. (B) Percent of freezing time during Reactivation and Test sessions expressed as mean ± S.E.M. (VEH, N = 8, VEH + DIST, N = 9, NIMO, N = 8, and NIMO + DIST, N = 8). (a) significantly different from both control groups, VEH and NIMO (P < 0.05; Newman-Keuls post-hoc test); (b) significantly different from all the other groups (P < 0.05; Newman-Keuls post-hoc test); (c) performance differs significantly between sessions (P < 0.05; Newman-Keuls post-hoc test).
