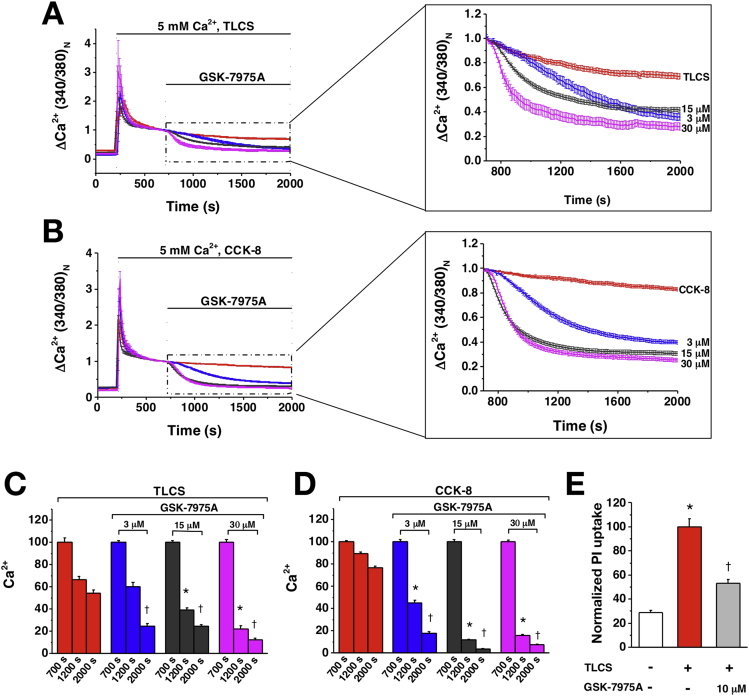
Figure 2.
GSK-7975A concentration-dependently inhibits CRAC entry (Fura-2 340:380 normalized at 700 s) and necrosis (PI uptake). Changes in mouse pancreatic acinar [Ca2+]C induced by (A) TLCS (500 μmol/L) and (B) CCK (1 nmol/L) showing effects of GSK-7975A from 700 s, expanded. (C and D) Mean (±SEM) [Ca2+]C at 700, 1200, and 2000 s from panels A and B, showing progressive reduction with increasing GSK-7975A (≥19 cells/group; *P < .001, toxin vs toxin plus GSK-7975A at 1200 s; †P < .001 at 2000 s). (E) GSK-7975A protected isolated murine pancreatic acinar cells from necrotic cell death pathway activation induced by TLCS (500 μmol/L) (mean ± SEM, normalized to TLCS at 100; ≥3 experiments/group; *P < .001, control vs TLCS; †P < .001, TLCS vs TLCS plus GSK-7975A).