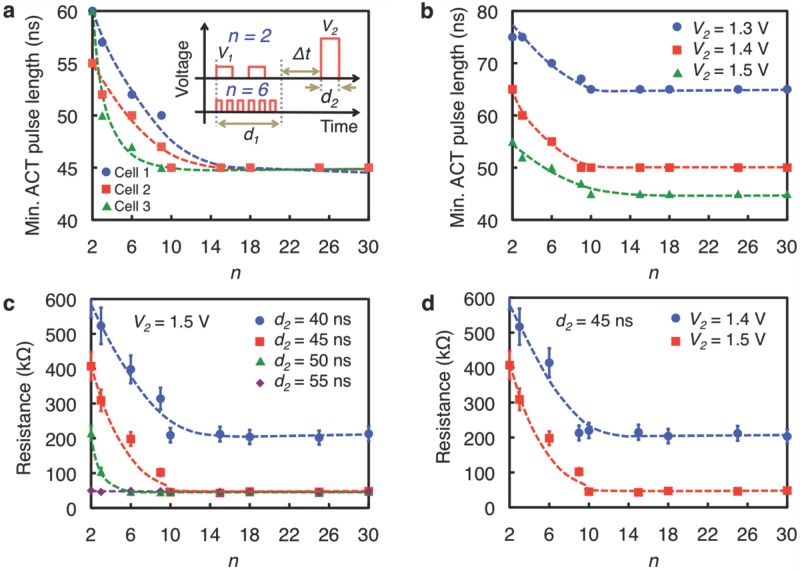
Figure 3.
Control of TA-states via frequency modulation of stimulus pulses. Dependence of the minimum ACT pulse length [a) and b)] and cell resistance [c) and d)] on the number of pulse periods n. The period number is controlled by varying both stimulus and inter-stimulus pulse lengths within a time frame of 900 ns. The stimulus and inter-stimulus pulse lengths are the same. The number of periods is given by the ratio of the time frame to the sum of the stimulus and inter-stimulus pulse lengths. The stimulus pulse voltages are 0.9 V, and the spacing between the chain of stimulus pulses and the ACT pulse is 1 s. The resistance state of a cell can be modulated by altering three independent parameters (i.e., n, V2 and d2).