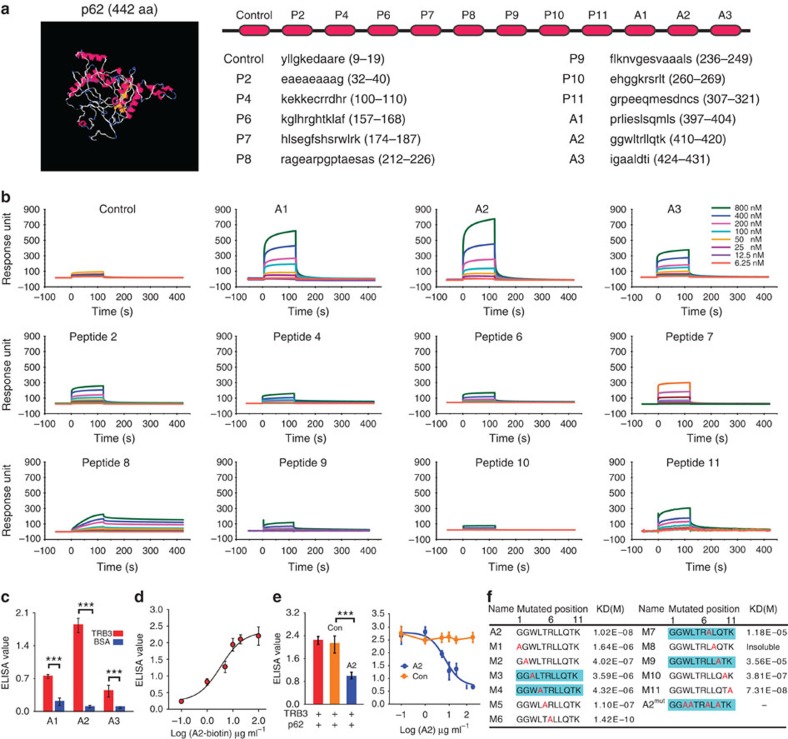
Figure 6. The TRB3-binding α-helical peptides are identified with the SPR screening.
(a) The 3D structure of P62 was predicted by the I-TASSER server and the amino-acid sequences of the indicated α-helical peptides from P62 were shown. (b) The indicated concentrations of the peptides were passed over immobilized TRB3 on CM5 sensor chips. (c) ELISA analysis of the binding ability of HRP-conjugated A1, A2 and A3 (10 μg ml−1) to purified TRB3 protein and a negative control BSA. Data are means±s.e.m. of three independent assays. Statistical significance was determined with Student's t-test; ***P<0.001. (d) The indicated concentration of HRP-conjugated A2 was incubated with TRB3, and the binding of A2/TRB3 was measured at 450 nm after reaction with HRP substrates. Data are means±s.e.m. of three independent assays. (e) The p62 binding to TRB3 was competed with 0.1–100 μg ml−1 of A2 or control peptide, and the binding of TRB3/p62 was detected using ELISA assay. Data are means±s.e.m. of three independent assays. (f) Each amino acid of A2 was substituted with alanine. Kinetic interactions of mutated peptides and TRB3 were determined by SPR analyses.