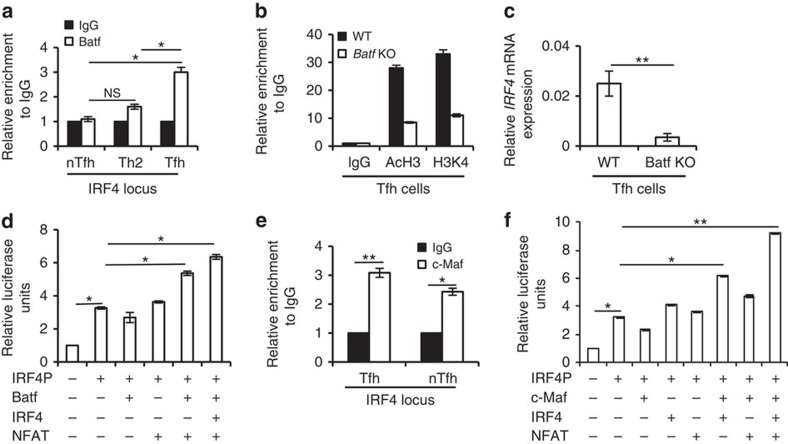
Figure 5. Batf and c-Maf regulate IRF4 expression.
(a) ChIP analysis of Batf binding in IRF4 locus in in vitro-differentiated Th2 cells and nTfh and Tfh cells isolated from Ova-immunized male WT (6–8 weeks old) mice. (b) ChIP analysis of active histone proteins (AcH3 and H3k4) at the IRF4 locus in Tfh cells isolated from Ova-immunized male WT and Batf KO (6–8 weeks old) mice. (c) IRF4 mRNA expression in Tfh cells isolated from Ova-immunized male WT and Batf KO mice. Data were normalized to beta-actin gene. (d) Luciferase assay in EL-4 cells transfected with IRF4 promoter containing luciferase vector along with expression plasmids of the indicated factors. Relative luciferase units are expressed as a fold difference to the control (pGL3) value. (e) ChIP analysis of c-Maf binding to the IRF4 locus in Tfh and nTfh cells isolated from Ova-immunized male WT (6–8 weeks old) mice. (f) Luciferase assay in EL-4 cells transfected with IRF4 promoter containing luciferase vector along with expression plasmids of the indicated factors. Relative luciferase units are expressed as a fold difference to the control (pGL3) value. Results shown are mean±s.e.m. and representative of at least three independent experiments. P values: *<0.05 and **<0.01. Student's t-test was performed to detect between-group differences.