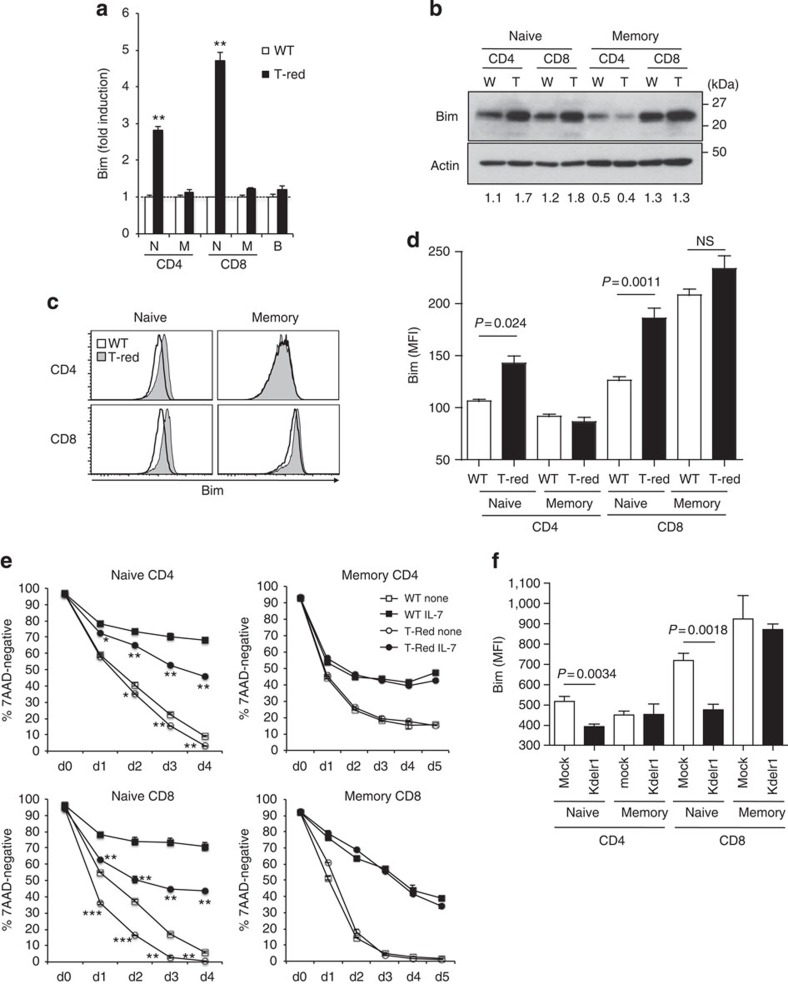
Figure 5. A functional defect in KDELR1 increases stress-mediated Bim expression and apoptosis in T-Red naïve T cells.
(a–d) Bim mRNA and protein levels were investigated by real-time PCR (a), western blot (b) and flow cytometry (c,d) in T-Red (T) and WT (W) mice (8–10 weeks old). N, M and B indicate naïve, memory and B cells, respectively. Expression levels of WT populations were normalized as 1 in a. Numbers in b represent the intensity ratio of Bim/Actin. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown in b,c. The mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of intracellular staining of Bim is shown in d (n=3–4). (e) In vitro survival of naïve and memory/activated T cells in the presence or absence of IL-7. Mice between 9 and 10 weeks old were used. (f) Bim expression in naïve and memory/activated T cells by flow cytometry following retrovirus-mediated forced expression of WT KDELR1 in T-Red haematopoietic stem cells and BMT (n=4). Mice between 6 and 8 weeks were used. Data represent the mean+s.d. (a,e) or s.e.m. (d,f). P values are shown in some figures. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. NS, not significant.