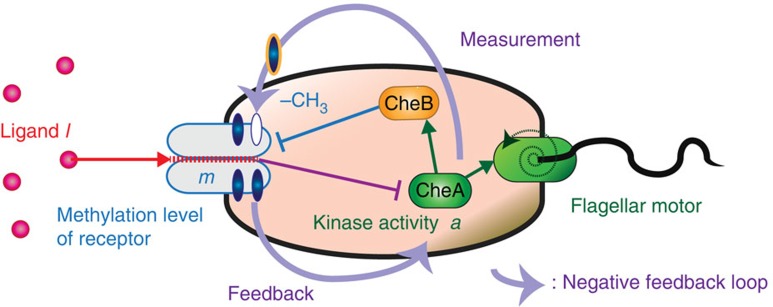
Figure 1. Schematic of adaptive signal transduction of E. coli bacterial chemotaxis.
Kinase activity a (green) activates a flagellar motor to move E. coli towards a direction of the higher ligand density l (red) by using the information stored in methylation level m (blue). CheA is the histidine kinase related to the flagellar motor, and the response regulator CheB, activated by CheA, removes methyl groups from the receptor. The methylation level m plays a similar role to the memory of Maxwell's demon 8,24, which reduces the effect of the environmental noise on the target system a; the negative feedback loop (purple arrows) counteracts the influence of ligand binding.