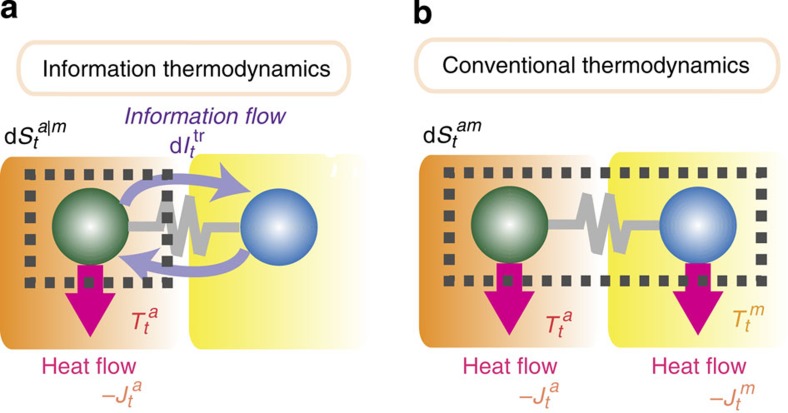
Figure 3. Schematics of information thermodynamics and conventional thermodynamics.
A green (blue) circle indicates subsystem a (m) and a grey polygonal line indicates their interaction. (a) The second law of information thermodynamics characterizes the entropy change in a subsystem in terms of the information flow between the subsystem and the outside world (that is, 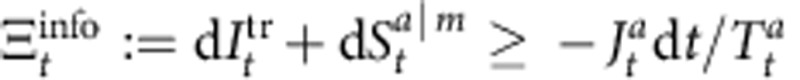 ). The information-thermodynamics picture concerns the entropy change inside the dashed square that only includes subsystem a. (b) the conventional second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy change in a subsystem is compensated for by the entropy change in the outside world (that is,
). The information-thermodynamics picture concerns the entropy change inside the dashed square that only includes subsystem a. (b) the conventional second law of thermodynamics states that the entropy change in a subsystem is compensated for by the entropy change in the outside world (that is, 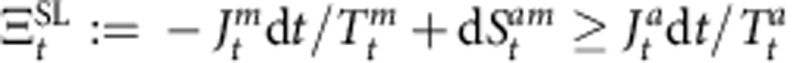 ). The conventional thermodynamics picture concerns the entropy change inside the dashed square, which includes the entire systems a and m. As explicitly shown in this paper, information thermodynamics gives a tighter bound of the robustness
). The conventional thermodynamics picture concerns the entropy change inside the dashed square, which includes the entire systems a and m. As explicitly shown in this paper, information thermodynamics gives a tighter bound of the robustness 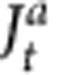 in the biochemical signal transduction of E. coli chemotaxis.
in the biochemical signal transduction of E. coli chemotaxis.