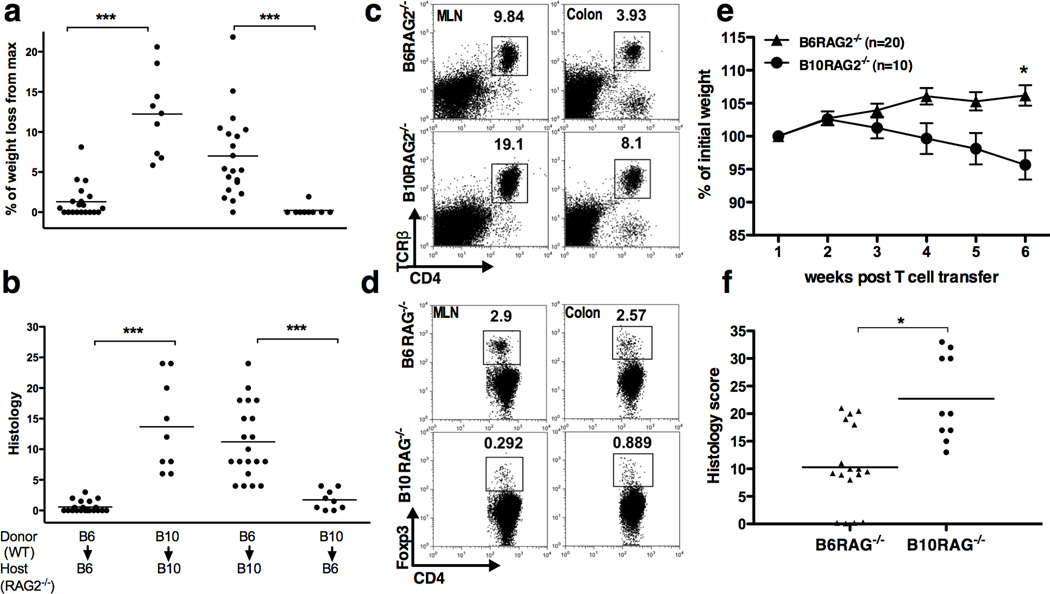
Figure 3.
Differential iTreg/pathogenic T cell balance and disease severity is host-dependent and T cell- and antigen-independent. (a) Weight change and (b) histology scores 7 weeks post-transfer of naïve T cells from B6 donors to B10-RAG−/− recipients and vise versa. One representative of two independent experiments with similar results is shown (9–20 mice per group) (c, d) Flow cytometry analysis of lymphocytes, gated based on characteristic light-scatter properties, isolated from the indicated organs of B6 and B10-RAG2−/− recipients of OT-II CD4+CD45RBhigh T cells followed by OVA feeding. One representative of two independent experiments is shown with 5 pooled mice per group per experiment. (e, f) Timed pregnant female mice from breeding pairs of B6 and B10 RAG−/− were co-housed together with their pups 3 days after giving the birth. Following weaning, the pups of each strain were separated, housed under the same conditions, and transferred CD4+CD45RBhigh T cells. Data are mean ± SD of 10–20 mice per group and representative of 2 independent experiments with similar number of mice in each. (e) Weight change after T cell transfer, (f) Colonic histology scores at study end-point (week 7). Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference between the two strains (*P<0.01, ***P<0.001).