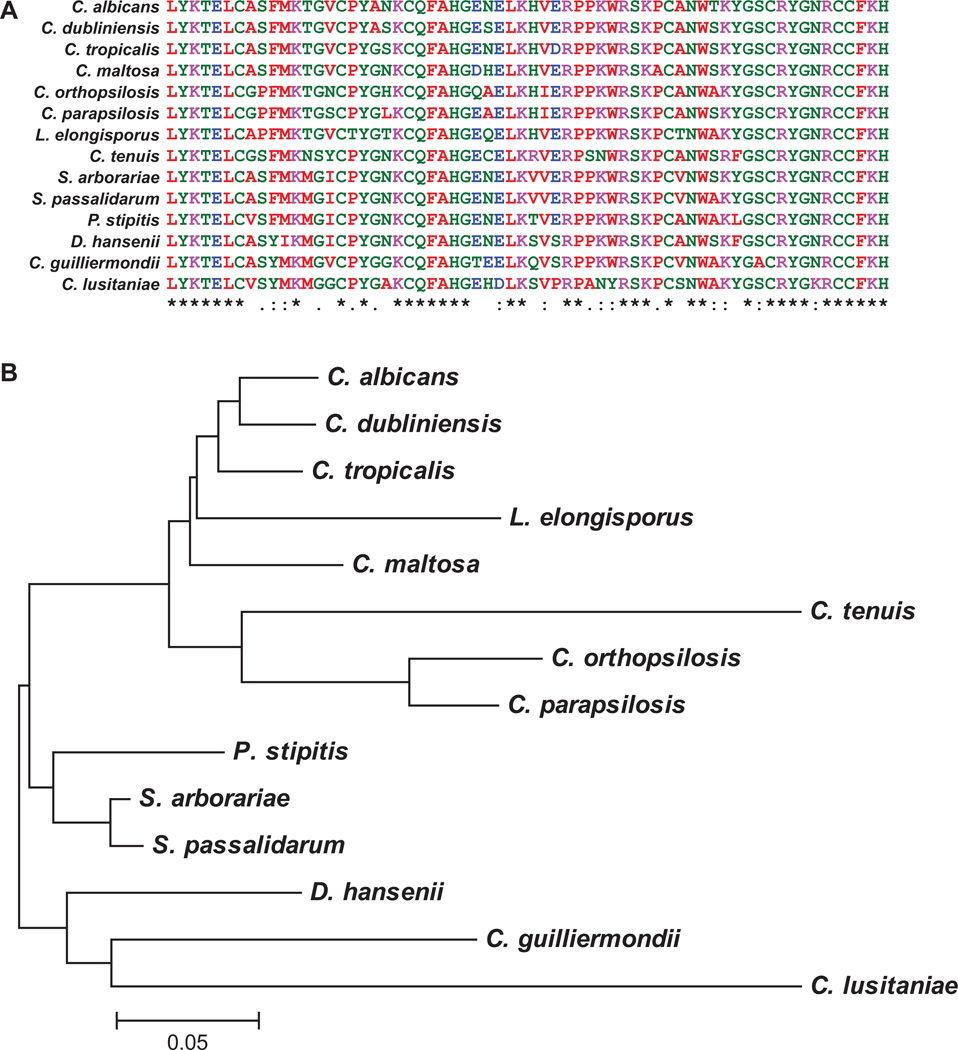
Fig. 6. Conservation of the TZF domain from Zfs1 across CTG clade species.
A. Shown is a sequence alignment of the TZF domain from Candida albicans Zfs1 and from the orthologous protein sequences from the indicated members of the CTG clade. Sequences were aligned by ClustalW2, and colors were assigned by ClustalW2 based on their physiochemical properties. Asterisks (*) indicate amino acid identity at that site; colons (:) indicate a conserved substitution; and dots (.) indicate a semi-conserved substitution at that site.
B. Shown is a phylogenetic tree, demonstrating the relatedness of the Zfs1 TZF domains within species of the CTG clade. This tree used only the TZF domain sequences shown in A. The sequence for each protein was obtained from GenBank as described in the Experimental procedures section, and sequence relationships were determined using the neighbor-joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987). The original alignment was performed in ClustalW2, and the tree was constructed in MEGA5.1. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Dayhoff matrix based method (Schwartz and Dayhoff, 1979). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths representing the number of amino acid substitutions per site.