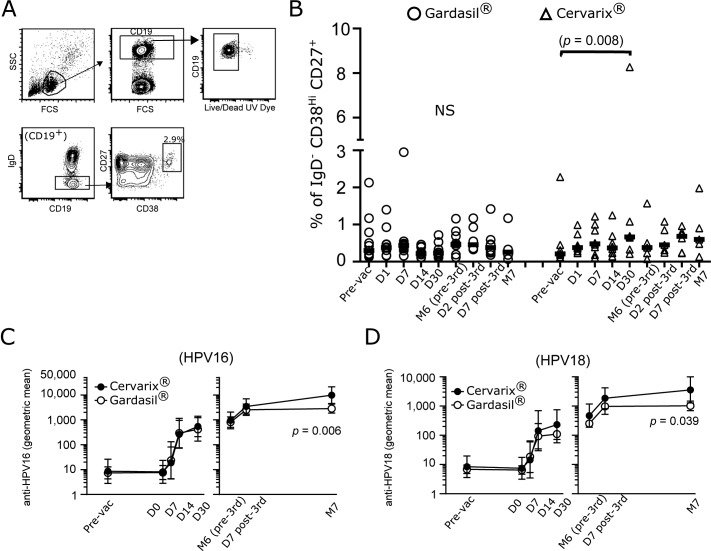
Fig 4. Generation of IgD-CD38HiCD27+ memory B cells after vaccination.
(A) Gating strategy used to identify IgD-CD38HiCD27+ memory B cells is shown. (B) Percentages of memory B cells in Gardasil or Cervarix immunized recipients were plotted over time. Statistical analyses were performed as described in Fig 3. Black bars indicate the medians. For the comparison of the two vaccine groups described in the “A higher frequency of IgD-CD38HiCD27+ memory B cells was present in Cervarix recipients at D30 post-first vaccination” section, paired, two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum analyses were performed. N = 10–11 (pre-vac to D30) and N = 6–8 (M6 to M7) for Gardasil. N = 8 (pre-vac to D30) and N = 5–6 (M6 to M7) for Cervarix. (C and D) ELISA were performed to determine the titers of anti-HPV16 (C) and-HPV18 (D) IgG. Geometric mean antibody titers (EU/ mL) ± 95% confidence intervals in log10 scale were plotted as a function of time. The plots on the left show the titers post-first vaccination, and the plots on the right show the titers after the third vaccination. Paired, two-tailed Wilcoxon rank sum analyses were performed. N = 12–15 Gardasil, and N = 8–12 for Cervarix.