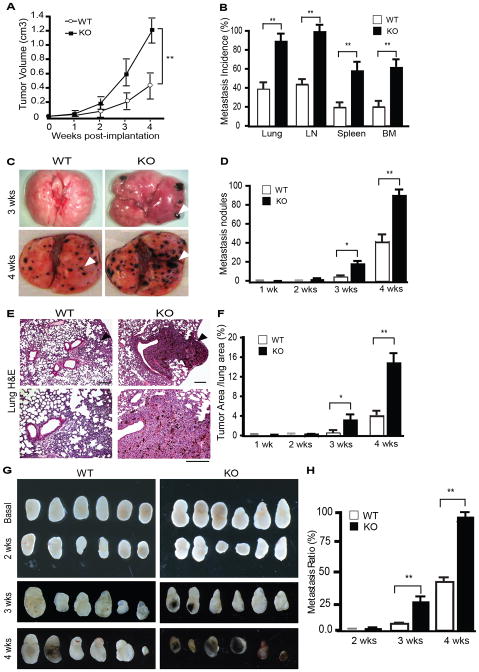
Figure 1. Augmented growth and metastasis of B16F10 melanoma in AIP1-KO mice.
B16 melanoma cells were injected subcutaneously (SQ) into WT and AIP1-KO mice. A. Tumor volumes are presented. n=10 mice per group. **, p<0.01. B. Tumor metastases to distant tissues were examined microscopically at week 2–4 post-implantation. Metastasis incidence (% of mice with detectable pigmented tumor nodules) was quantified. Data for week 4 are shown. n=10 mice per group. **, p<0.01. C. Representative images of tumor metastasis at week 3 and 4 in lung are shown. Arrowheads indicate the tumor nodules. D. Lung metastasis nodules at 4 weeks were quantified. n=10 mice per group. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01. E. Lung metastasis was examined by H&E staining. F. Metastatic tumor areas in lung were quantified from 5 random fields per lung and n=5 mice per group. *, p<0.05 and **, p<0.01. Scale bar: 50 μm. G. Regional inguinal lymph nodes were excised from WT and KO at basal or 2–4 weeks after tumor implantation; note that the pigmented melanoma metastases were detected at 3 and 4 weeks in AIP1-KO but only visible at 4 weeks in WT mice. H. LN metastases were quantified. n=10 mice per group. **, p<0.01.