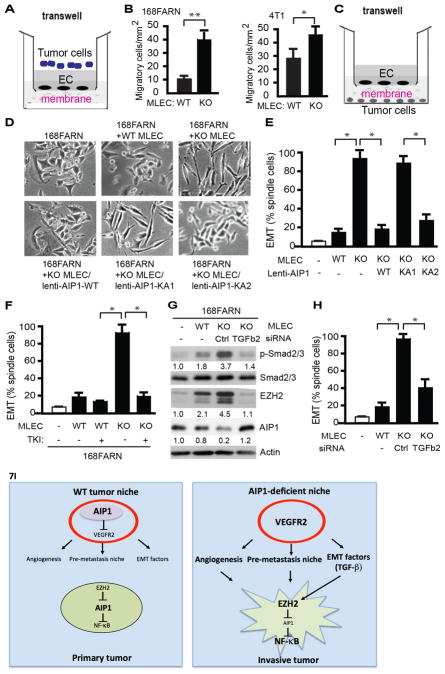
Figure 7. AIP1-VEGFR2 signaling in vascular EC regulates tumor cell EMT program.
A–B. Endothelial permeability - tumor cell invasion assay. WT or AIP1-KO MLECs cells were cultured on the top of the transwell as monolayer for 2 days post-confluency. Tumor cells (168FARN or 4T1) were seeded at the top well of the Boyden Chamber and cells that transmigrated cross the endothelium layer were quantified at 12 h. Data presented in B are mean ± SEM from duplicates and three independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. C. Diagram for the co-culture assay. MLECs were seeded at the top of the transwell. Tumor cells (e.g., breast cancer cell line 168FARN) were seeded at the bottom well of the Boyden Chamber. The two types of cells were grown without direct cell-to-cell contact and separated by a membrane with 0.4 μm pore size permeable for molecules but not for cells. D–E. Effect of MLECs on tumor cells. Co-culture of breast cancer cell line 168FARN with MLECs isolated from WT mice, AIP1-KO mice, AIP1-KO MLECs with a re-expression of AIP1, AIP1-KA1 or AIP1-KA2 by lentivirus. At 12 h, cell morphological analyses of co-cultured 168FARN cells were performed under light microscopy. Representative images are from 1 of 3 independent experiments (B). Quantifications of EMT (% of elongated spindle cells) are presented. Data are mean ± SEM from duplicates and three independent experiments. *, p<0.05. F. VEGFR2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) diminished the effects of AIP1-KO MLECs on 168FRAN. Co-culture of breast cancer cell line 168FARN for 12 h with MLECs isolated from WT mice or AIP1-KO mice in the presence or absence of VEGFR2 TKI (20 μM). Tumor cell EMT based on morphological analyses were quantified. Data are mean ± SEM from duplicates and three independent experiments. *, p<0.05. G–H. TGFβ2 mediates MELC-enhanced tumor EMT responses. Co-culture of 168FARN with WT MLECs, AIP1-KO MLECs or AIP1-KO MLECs with TGFβ2 siRNA knockdown for 12 h. Phosphorylation of Smad2/3, expression of EZH2 and AIP1 in co-cultured 168FARN cells were determined by Western blot with respective antibodies. Fold changes are presented from 1 of 3 independent experiments, taking 168FARN alone as 1.0 (G). 168FARN cell morphological analyses were performed under light microscopy and quantifications of EMT are presented. Data are mean ± SEM from duplicates and three independent experiments. *, p<0.05. I. Models for the role of stromal AIP1-VEGFR2 signaling in regulation of tumor cell EMT and metastasis. In WT tumor niche, AIP1 inhibits VEGFR2 to repress tumor angiogenesis, pre-metastatic niche formation and tumor EMT switch. In AIP1-deficeint tumor niche, enhanced VEGFR2 signaling induces tumor angiogenesis and formation of pre-metastatic niche. Enhanced VEGFR2 activity in vascular EC also stimulates secretion of tumor EMT-promoting factors (e.g., TGFβ2), which directly augment tumor cell EMT phenotypic changes, including upregulation of EZH2 protein, reduction of AIP1 protein, increases in NF-κB activity and NF-κB-dependent IL-6 expression. Together, AIP1-deficeint niche promotes tumor invasion and metastasis.