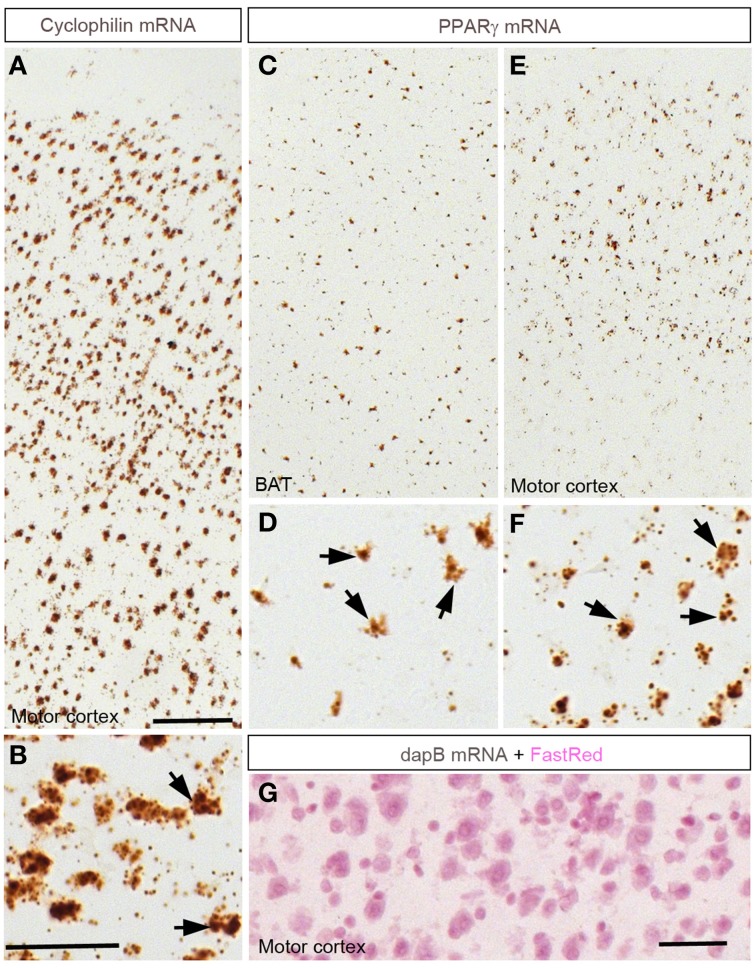
Figure 1.
Chromogenic detection of PPARγ in the mouse brain. (A,B) Hybridization signals (brown) of Ppib in the motor cortex. As expected, Ppib was ubiquitously expressed across the entire brain including the cortex. (C,D) PPARγ hybridization signals in the brown adipose tissue (BAT). Presumptive adipocytes abundantly expressed PPARγ. (E,F) PPARγ hybridization signals in the cortex. Note that PPARγ expression was systematically higher in the outer layers of the neocortex. Black arrows indicate representative Ppib- or PPARγ–expressing cells. (G) Absence of signals in the neocortex hybridized with a probe against dapB and counterstained with Fast-Red. Minor adjustments in contrast or brightness were made uniformly. Abbreviations: BAT, brown adipose tissue; Scale bar in (A,C,E) is 120 μm; in (B,D,F) is 40 μm; in (G) is 50 μm.