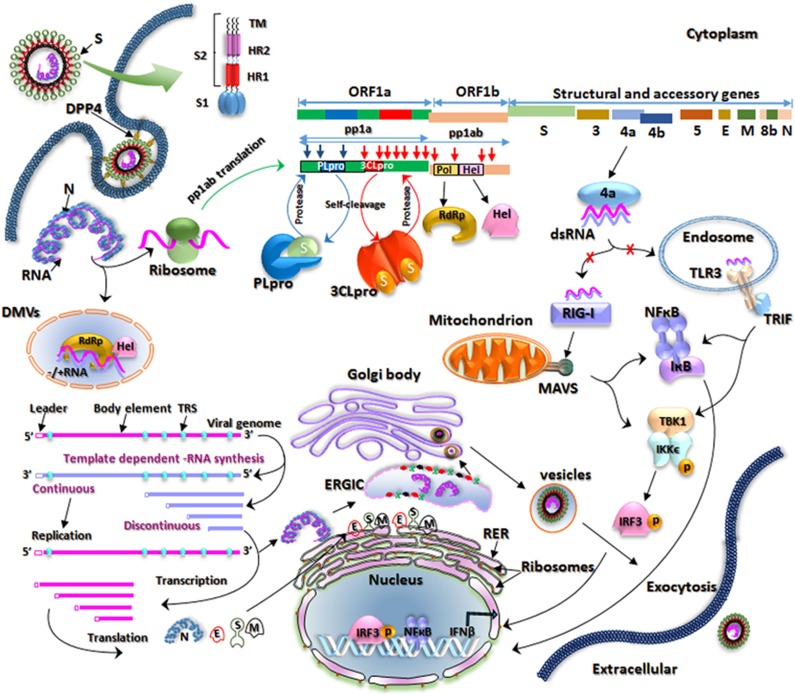
Figure 3.
Schematic of the replication cycle of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). MERS-CoV binds to dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) on the host cell through its receptor-binding domain (RBD) in the S1 subunit of the spike (S) glycoprotein, which leads to virus–cell fusion and the release of genomic RNA into the cytoplasm. Initially open reading frame 1a (ORF1a) and ORF1b are translated into polyproteins, polyprotein 1a (pp1a) and pp1ab, respectively, which are cleaved by the virus-encoded proteases papain-like protease (PLpro) and 3C-like protease (3CLpro) into 16 mature nonstructural proteins (nsps). The proteins involved in replication and transcription are gathered into replication-transcription complexes (RTCs) that associate with double-membrane vesicles (DMVs) derived from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The genomic RNA contains adenylate uridylate (AU)-rich sequences called transcription regulation sequences (TRSs). If the TRSs are recognized by RTCs, then RNA of subgenomic length for transcription will be generated, otherwise a full-length template RNA of genomic length for replication will be synthesized. The newly produced genomic RNAs are encapsidated in the nucleocapsid (N) proteins in the cytoplasm and then transported to the ER–Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) for further assembly. The S, membrane (M) and envelope (E) proteins are inserted into the membrane of the rough ER (RER), from where they are transported to the ERGIC to interact with the RNA-encapsidated N proteins and assemble into viral particles. The budded vesicles containing mature viral particles are then transported to the cell surface for release after maturation in the Golgi bodies. Double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) are partially generated during viral replication. The 4a competes with Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and retinoic acid-inducible gene I product (RIG-I)-like helicases (RIG-I and melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5 (MDA5)) to bind to dsRNAs and evades the host immune response.