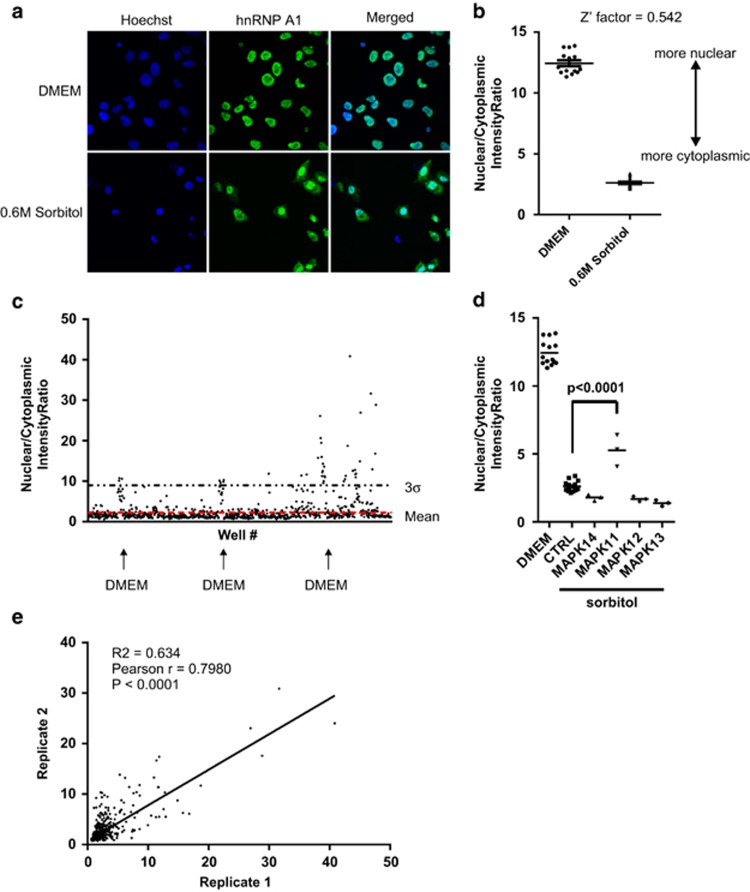
Figure 1.
RNAi screen identifies several candidate kinases that regulate cytoplasmic accumulation of hnRNP A1 in response to hypertonic stress. (a) U2OS cells were treated with 0.6 M sorbitol for 4 h and the subcellular localization of hnRNP A1 was determined by immunofluorescence. Nuclei were visualized with Hoechst staining. (b) The nuclear/cytoplasmic intensity ratio of hnRNP A1 distribution in experiment (a) was determined as described in the Materials and Methods and the robustness of the assay was determined by the Z'-factor as previously described.32 (c) U2OS cells were reverse transfected for 72 h with a library of siRNA pools against 691 human kinases and kinase-related genes (the kinome subset of the Qiagen Human Druggable Genome siRNA Set Version 2.0) and subsequently treated with 0.6 M sorbitol for 4 h. The nuclear/cytoplasmic intensity ratio of hnRNP A1 was determined as in (b) and plotted. Each dot represents an siRNA pool. The red line represents the mean of nuclear/cytoplasmic intensity ratios across all plates. The dotted black line represents 3σ. Clusters of wells treated with DMEM instead of sorbitol are indicated with black arrows. Results from one replicate are shown. (d) The nuclear/cytoplasmic intensity ratio of hnRNP A1 for siRNA pools targeting the four members of the p38 MAPK family (MAPK14, MAPK11, MAPK12, and MAPK13) from all three replicates is shown. (e) Correlation plot between two replicates of the RNAi screen. Each dot represents an siRNA pool