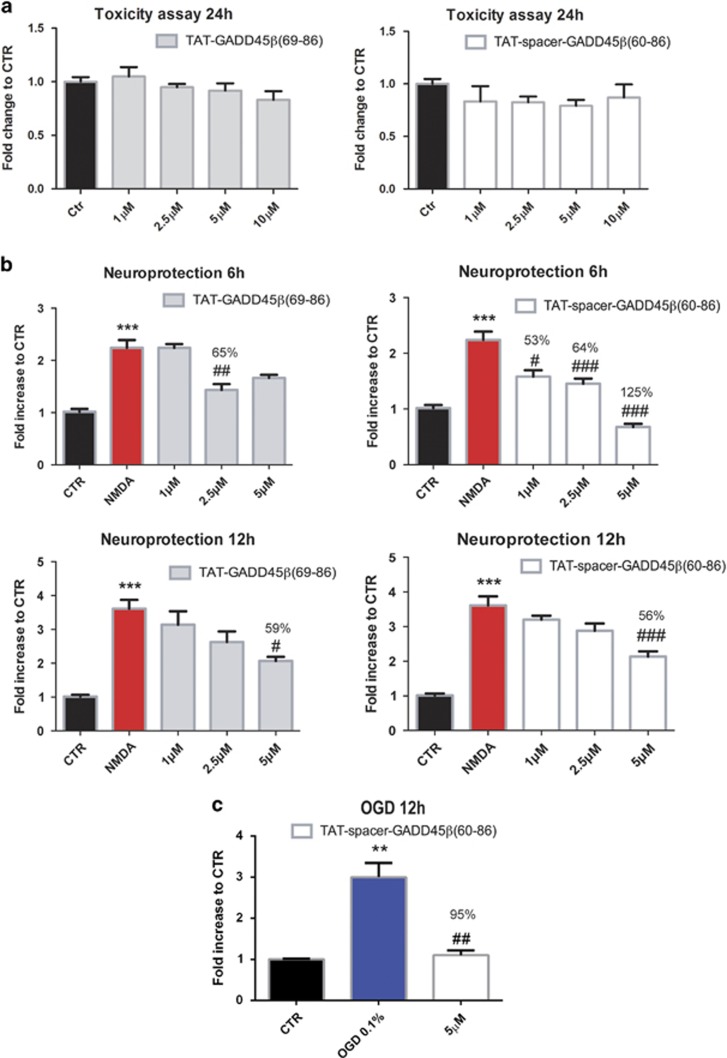
Figure 3.
TAT-GADD45β69–86 and TAT-spacer-GADD45β60–86 do not induce neuronal death and protect neurons from NMDA and OGD insults. (a) LDH assay to assess intrinsic toxicity of MKK7 inhibitor peptides. Twelve DIV cortical neurons were treated with increased concentrations (1, 2.5, 5 and 10 μM) of TAT-GADD45β69–86 (left) and TAT-spacer-GADD45β60–86 (right) for 24 h. Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (one-way ANOVA, P>0.05, n=8). (b) LDH assay was performed on 12 DIV cortical neurons to evaluate the ability of TAT-GADD45β69–86 (left) and TAT-spacer-GADD45β60–86 (right) peptides (1, 2.5 and 5 μM) to protect against 100 μM NMDA-induced excitotoxicity in vitro for 6 (upper panels) and 12 h (lower panels). Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-hoc test, ***P<0.001 NMDA versus CTR, #P<0.05 NMDA+MKK7I versus NMDA, ##P<0.01 NMDA+MKK7I versus NMDA, ###P<0.001 NMDA+MKK7I versus NMDA, n=6). (c) LDH assay to evaluate the ability of TAT-spacer-GADD45β60–86 peptide pre-treatment (5 μM, 30 min before OGD) to protect against 12 h OGD. Data are presented as mean±S.E.M. (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-hoc test, **P<0.01 OGD versus CTR, ##P<0.01 OGD+MKK7I versus OGD, n=6)