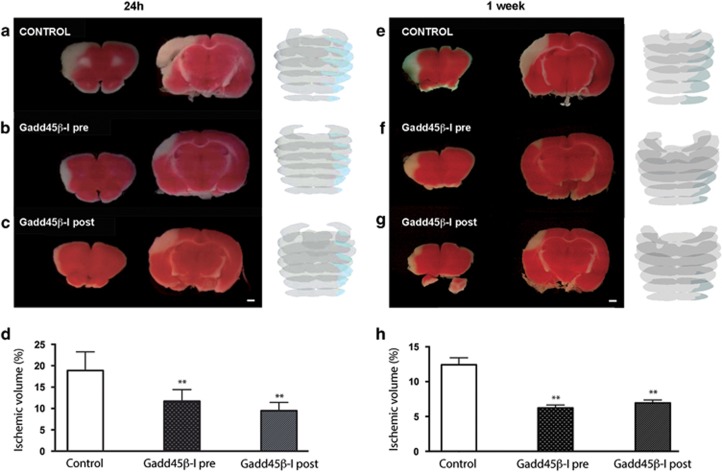
Figure 5.
GADD45β-I protects against MCAO. Rats were injected with (a) vehicle or with (b) GADD45β-I (11 mg/kg) 30 min before lesion or with (c) GADD45β-I (11 mg/kg) 6 h after lesion. All groups were killed 24 h after lesion. Brains were extracted and colored with TTC staining to reveal ischemic areas. Ischemic volume was measured for all the three experimental groups with NIH ImageJ analysis software. Images 4A–C are TTC-stained slices at different levels of a representative animal for each different groups (scale bar 1mm). In addition, we show a full reconstruction of the lesion size (blue shade on gray) obtained with contour analysis through Neurolucida software. (d) Percentage of ischemic volume for the two groups (GADD45β-I 30 min before lesion n=6 and GADD45β-I 6 h after lesion n=5) of treated animals was compared with untreated animals (n=6). Data represent mean±S.D.; one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's post-hoc test, **P<0,01. Rats were injected with (e) vehicle 30 min before lesion or with (f) GADD45β-I (11 mg/kg) 30 min before lesion, or with (g) GADD45β-I (11 mg/kg) 6 h after lesion. All groups were killed 24 h after lesion. Brains were extracted and colored with TTC staining to reveal ischemic areas. Ischemic volume was measured for all the three experimental groups with NIH ImageJ analysis software. Images 4A–C are TTC-stained slices at different levels of a representative animal for each different groups (scale bar=1 mm). In addition, we show a full reconstruction of the lesion size (blue shade on gray) obtained with contour analysis through Neurolucida software. (h) Percentage of ischemic volume for the two groups (GADD45β-I 30 min before lesion n=5 and GADD45β-I 6 h after lesion n=5) of treated animals was compared with untreated animals (n=5). Data represent mean±S.D.; one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's post-hoc test, **P<0.01