Figure 1. Gene and protein structure analyses of PxABCH1 in P. xylostella.
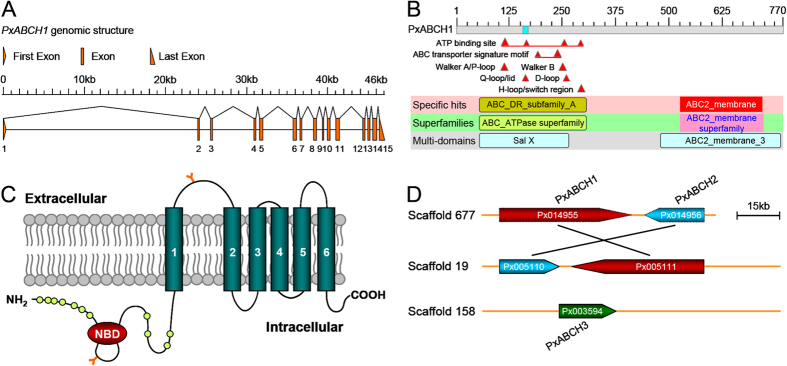
(A) Genomic structure of the PxABCH1 gene. Brown boxes indicate the exons, and the spaces between two boxes are the introns. The figure is drawn to scale, and the scale bar is shown. (B) NCBI conserved domain database (CDD)-based annotation of the deduced PxABCH1 protein sequence. Based on its sequence, the PxABCH1 protein was identified as a member of the ABC transporter superfamily and contains Sal X and ABC2_membrane_3 multi-domain regions, which are characteristic of the ABC-type transport system. The specific hits incorrectly denoted it as a member of the ABCA subfamily probably because of the high sequence similarity between members from ABCH and ABCA transporter subfamilies. Segments of the sequence with low compositional complexity are colored blue. (C) Predicted protein topology of the PxABCH1 protein. The protein contains one NBD and one TMD with six membrane-spanning segments. “Y” represents predicted N-glycosylation sites, and circles indicate potential O-glycosylation sites. (D) Structure and location of the ABCH genes on P. xylostella genome scaffolds. Three ABCH genes including PxABCH1 (Px014955 on scaffold_677 or Px005111 on scaffold_19), PxABCH2 (Px014956 on scaffold_677 or Px005110 on scaffold_19) and PxABCH3 (Px003594 on scaffold_158) are found in the P. xylostella genome database (DBM-DB: http://iae.fafu.edu.cn/DBM/index.php). The transcription orientations of these ABCH genes on the scaffolds are shown, and the PxABCH1 and PxABCH2 genes are tandemly arranged in a head-to-tail orientation.
