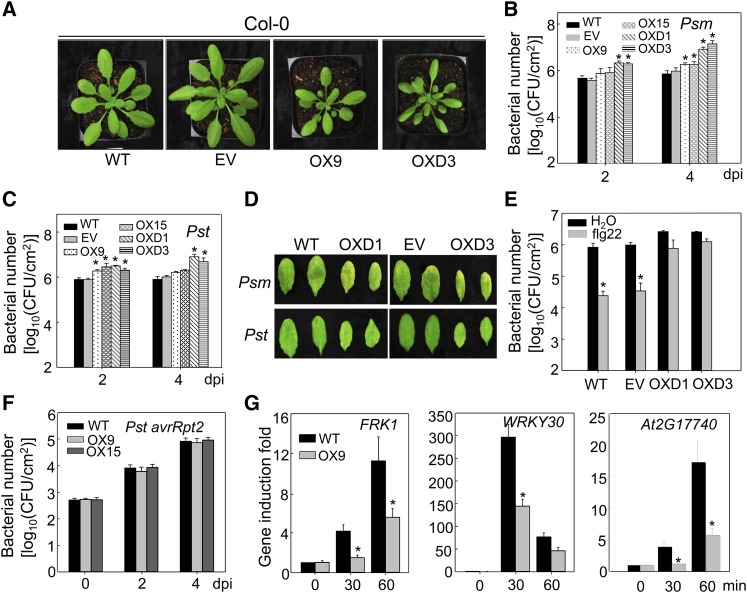
Figure 7.
Overexpression of ASR3 Compromises Disease Resistance to Virulent Bacterial Pathogens.
(A) Morphological phenotype of wild-type, the empty vector control (EV), 35S:ASR3-HA (OX9), and 35S:ASR3T189D-HA (OXD3) transgenic lines. Four-week-old soil-grown plants are shown.
(B) and (C) Bacterial multiplication of Psm ES4326 (B) or Pst DC3000 (C) in wild-type, empty vector control, 35S:ASR3-HA (OX9 and OX15), and 35S:ASR3T189D-HA (OXD1 and OXD3) transgenic plants at 2 and 4 dpi. Leaves from 4-week-old plants were hand-inoculated with Psm or Pst at 5 × 105 cfu/mL, and bacterial counting was performed at the indicated time points.
(D) The disease symptoms upon Psm or Pst infection. The pictures were taken at 4 dpi.
(E) Compromised flg22-mediated immunity to Pst infection in ASR3T189D overexpression lines. Leaves from 4-week-old plants were hand-inoculated with water or 100 nM flg22, and 24 h later hand-inoculated with Pst at 5 × 105 cfu/mL. Bacterial counting was performed at 3 dpi.
(F) Bacterial growth of Pst avrRpt2. The bacteria at 5 × 105 cfu/mL were hand-inoculated into leaves of 4-week-old plants.
(G) Reduced immune gene expression in ASR3 overexpression lines. Ten-day-old seedlings were treated with 100 nM flg22 for 30 and 60 min for qRT-PCR analysis. Gene expression level was normalized with internal control UBQ10.
The data in (B), (C), and (E) to (G) are shown as means ± sd from three biological repeats. The asterisk indicates a significant difference with a Student’s t test (P < 0.05) when compared with the wild-type or control treatment. The above experiments were repeated three times with similar results.