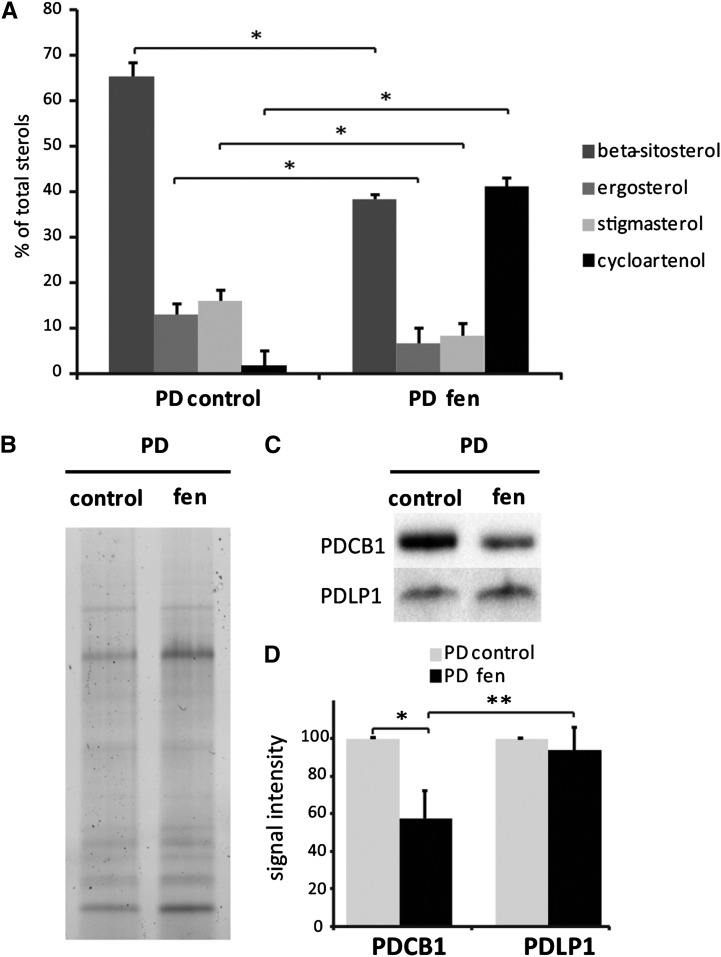
Figure 9.
Modification of the Sterol Pool of the PD-PM Domain Correlates with a Reduction of PDCB1 Association with PD Channels.
(A) Quantification by GC-MS of the sterol lipids in PD-enriched membrane fractions purified from control and fen-treated liquid cultured Arabidopsis cells (48 h, 250 μg/mL). Sterol inhibitor treatment leads to a strong decrease of total sterols and a concomitant increase of intermediate cyclopropyl sterols. n = 3 for PD and PD + fen samples. Error bars indicate sd.
(B) to (D) Immunoblot analysis of control and fen-treated PD fractions showing that, upon modification of the sterol pool, the PDCB1 association with PD channels is reduced, whereas the PDLP1 signal remains stable. (B) shows SDS-PAGE protein profiles of the PD- and PD-fen-treated fractions used for blotting shown in (C). (C) shows representative immunoblots for PDCB1 and PDLP1. (D) shows the quantification from immunoblot analyses of the PDCB1 and PDLP1 association with PD using the Bio-Rad Chemidoc MP system and Image Lab software.
Asterisks indicate significant differences (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01) using the Wilcoxon test. n = 3 for PD and n = 6 PD + fen samples. Error bars indicate sd.