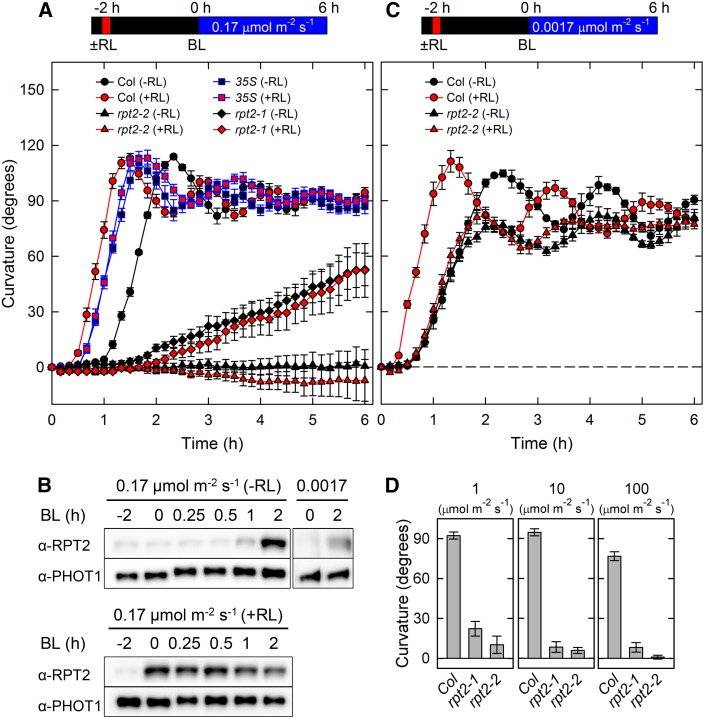
Figure 1.
Continuous Light-Induced Second Positive Phototropism in the rpt2 Mutants and the RPT2 Overexpression Line.
(A) Time-course analysis of continuous light-induced phototropism. Two-day-old dark-grown seedlings (Columbia [Col; circles], rpt2-2 [triangles], rpt2-2 transgenic plants harboring 35Spro:RPT2 [35S; squares], and rpt2-1 [diamonds]) were pretreated with (red symbols) or without (black symbols) overhead red light (RL) at 20 μmol m–2 s–1 for 2 min. The hypocotyls were then irradiated with unilateral blue light (BL) at 0.17 μmol m–2 s–1 for 6 h, during which time the hypocotyl curvatures were determined at 10-min intervals. The data shown are means ± se from eight seedlings.
(B) Effects of light irradiation on levels of RPT2. Dark-grown seedlings were pretreated with (top panel) or without (bottom panel) overhead red light for 2 min. After 2 h, seedlings were continuously irradiated with unilateral blue light at 0.17 or 0.0017 μmol m–2 s–1. The shoots were harvested at the indicated time points and used to prepare crude microsomal insoluble proteins. Proteins (6 μg) in each fraction were separated on 7.5% SDS-PAGE gels, followed by immunoblotting with anti-RPT2 and anti-PHOT1 antibodies. Time 0 corresponds to the onset of unilateral blue light treatment.
(C) Time-course analysis of continuous light-induced phototropism at 0.0017 μmol m–2 s–1. The data shown are means ± se from eight seedlings. Other details are as described in Figure 1A.
(D) Hypocotyl phototropism induced by strong blue light. Dark-grown seedlings were irradiated with unilateral blue light for 6 h at 1, 10, and 100 μmol m–2 s–1. The data shown are means ± se from 10 seedlings.