Figure 3.
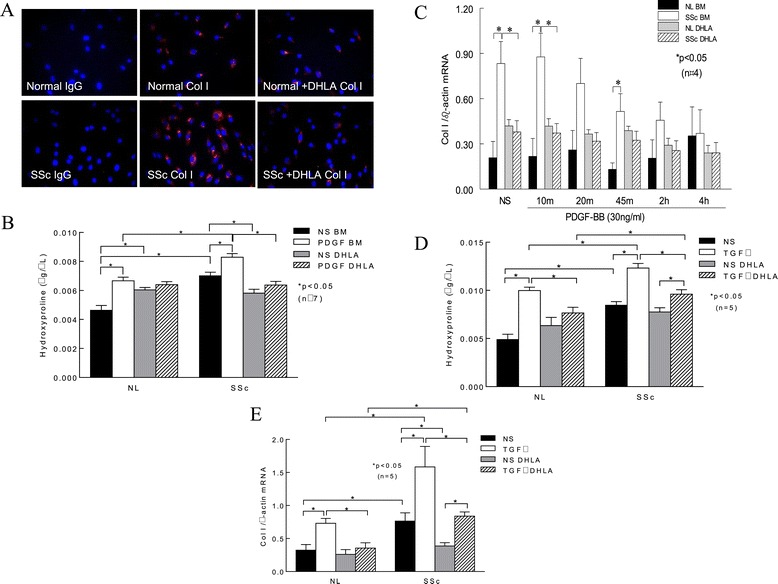
The expression of type I collagen in fibroblasts. (A) Immunostaining of type I collagen (Col I) in normal (NL) and scleroderma (SSc) dermal fibroblasts (n = 3 NL and 4 SSc subjects). IgG, Immunoglobulin G. (B) Hydroxyproline content was measured in cell culture media. As illustrated by the images shown in (A), hydroxyproline levels were elevated in SSc dermal fibroblasts compared to NL cells. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) significantly increased hydroxyproline in both NL and SSc cells. Addition of dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA) significantly reduced hydroxyproline in both NL and SSc cells. (C) Col I mRNA levels with or without PDGF stimulation at various time points. (D) The effect of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) on hydroxyproline levels was examined. TGF-β significantly increased hydroxyproline levels in both NL and SSc dermal fibroblasts, whereas DHLA decreased it. (E) TGF-β induced Col I mRNA levels in both NL and SSc fibroblasts, and DHLA decreased them significantly. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. P < 0.05 was considered significant. BM, Basal medium; NL, Normal; NS, Nonstimulated.
