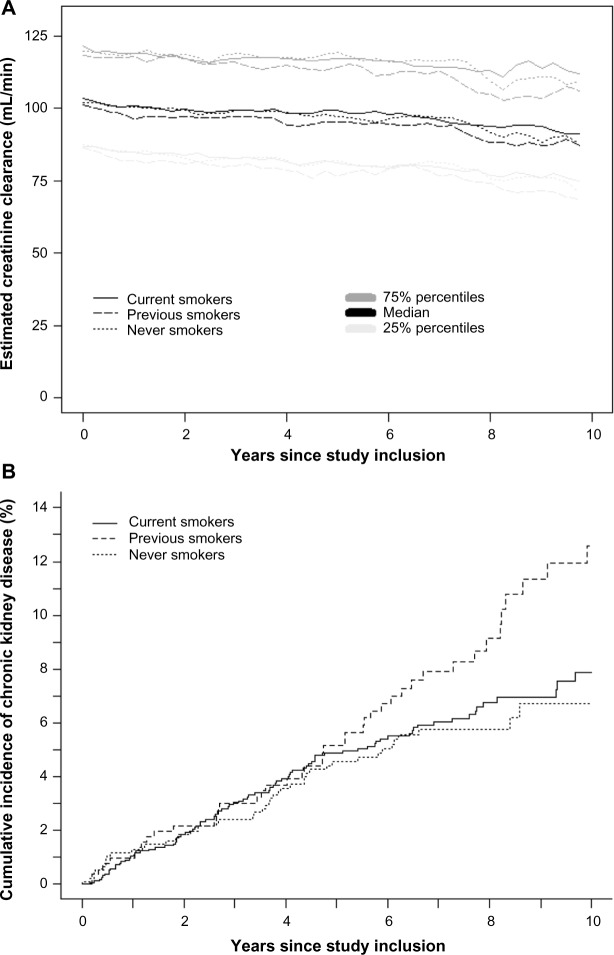
Figure 1.
Estimated creatinine clearance and risk of chronic kidney disease stratified on smoking status.
Notes: (A) 25%, median, and 75% percentiles of estimated creatinine clearance stratified on smoking status. We used the Cockcroft–Gault equation to calculate estimated creatinine clearance (displayed as mL/min) as estimate of glomerular filtration rate. We divided time from study inclusion until end of follow-up in 3-month intervals. In each interval, all participants contributed with one CG-CrCl. The CG-CrCl in a time interval was either the median of all CG-CrCls in that time interval. If no CG-CrCl was available in a 3-month time interval, the CG-CrCl was calculated as the weighted mean of the CG-CrCl measurements determined before and after the actual 3-month period. At study inclusion, there were 984 never smokers, 530 previous smokers, and 1,628 current smokers. At 10 years of follow-up, 110 never smokers, 98 previous smokers, and 170 current smokers were still under follow-up. (B) Risk of chronic kidney disease stratified on smoking status. Definition of chronic kidney disease: two consecutive CG-CrCls of ≤60 mL/min ≥3 months apart.
Abbreviation: CG-CrCl, estimated creatinine clearance calculated with the Cockcroft–Gault equation.