Figure 2.
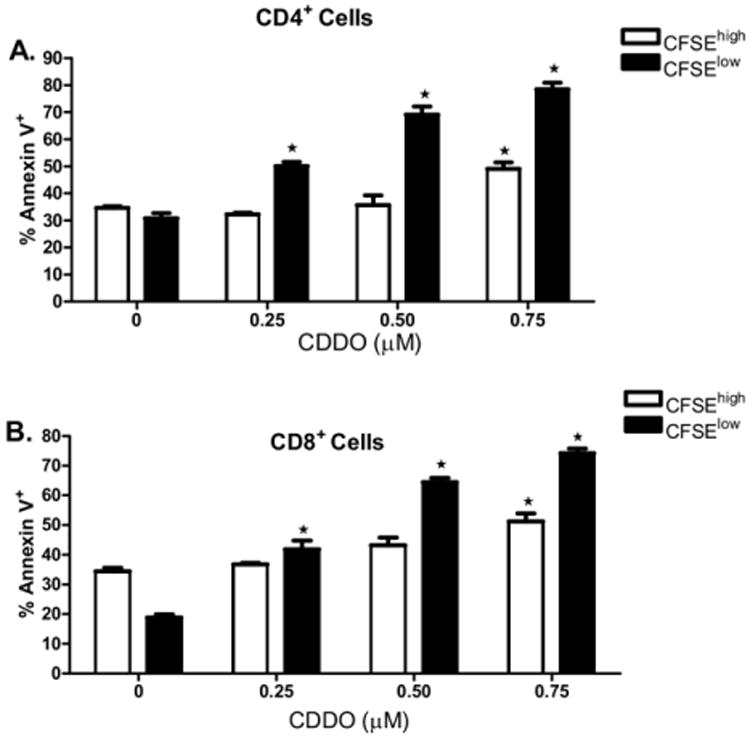
Proliferating, and not resting, T cells are highly sensitive to CDDO-mediated apoptosis. CFSE-labeled BALB/c splenocytes were incubated with irradiated T cell-depleted B6 splenocytes at a 1:1 ratio with a dose range of CDDO as described in Materials and Methods. After 3 days in culture, cells were harvested and analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were first gated on CD4 or CD8 expression, then gated on CFSEhigh or CFSElow staining, and analyzed for annexin V binding in proliferating or resting T cells. (A) Proportionally greater increases in annexin V binding were observed on proliferating (CFSElow) compared with nonalloreactive (CFSEhigh) CD4+ T cells with exposure to 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, and 0.75 μM CDDO. (B) Proportionally greater increases in annexin V binding were observed on proliferating (CFSElow) compared with nonalloreactive (CFSEhigh) CD8+ T cells with exposure to 0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, and 0.75 μM CDDO. *Significant differences of annexin V binding on CDDO-exposed T cells compared with control (P < 0.05). Results from 1 of 3 independent experiments are presented.
