Figure 3.
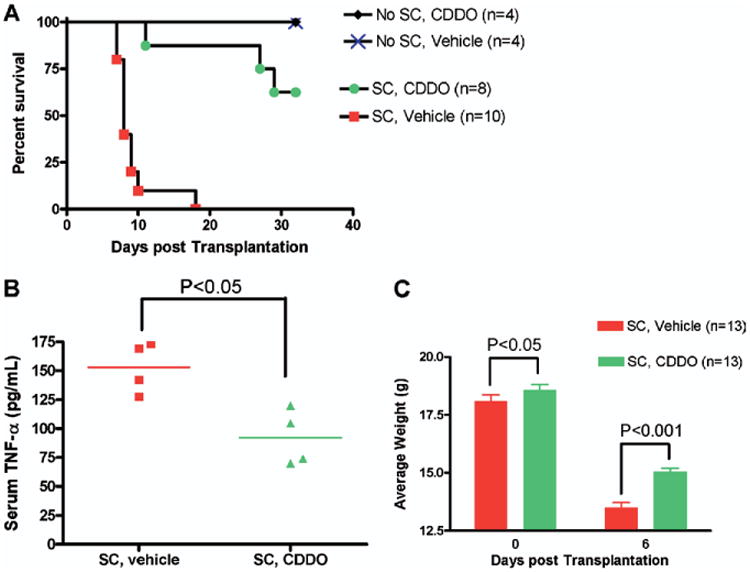
CDDO administration immediately after transplantation results in delayed development of GVHD and significant improvement in survival. B6 (H2b) mice received TBI (900 cGy) followed by infusion of 10 × 106 10 BALB/c (H2d) BMC and 35 × 106 BALB/c SC. Mice were treated with vehicle control or CDDO (240 μg/dose) twice a day intraperitoneally on day 0 and day +1 for a total of 4 doses. (A) Administration of CDDO protected mice from early GVHD mortality. Significant improvement in survival were observed in CDDO-treated mice (●) compared with GVHD control (vehicle control-treated) mice (■; P < .001). Results from 1 of 3 independent experiments are presented. (B) Significant decrease in serum TNF-α levels of mice on day +5 post-BMT in mice that received CDDO compared to mice treated with vehicle. (C) Significant protection from GVHD associated weight loss on day 6 post-BMT in mice that received CDDO. Mean body weights from 1 of 3 independent experiments are presented.
