Fig. 1.
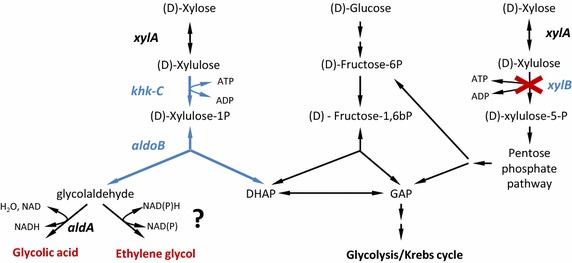
Synthetic (blue) and natural (black) d-xylose assimilation pathways. In the synthetic pathway (d)-xylose is transformed to (d)-xylulose by endogenous xylose isomerase (XylA). (d)-xylulose-1-kinase (Khk-C) phosphorylates (d)-xylulose to obtain (d)-xylulose-1P, and (d)-xylulose-1-phosphate aldolase (Aldo-B) cleaves (d)-xylulose-1P into glycolaldehyde and DHAP. Ethylene glycol is produced via the action of an unknown endogenous aldehyde reductase.
