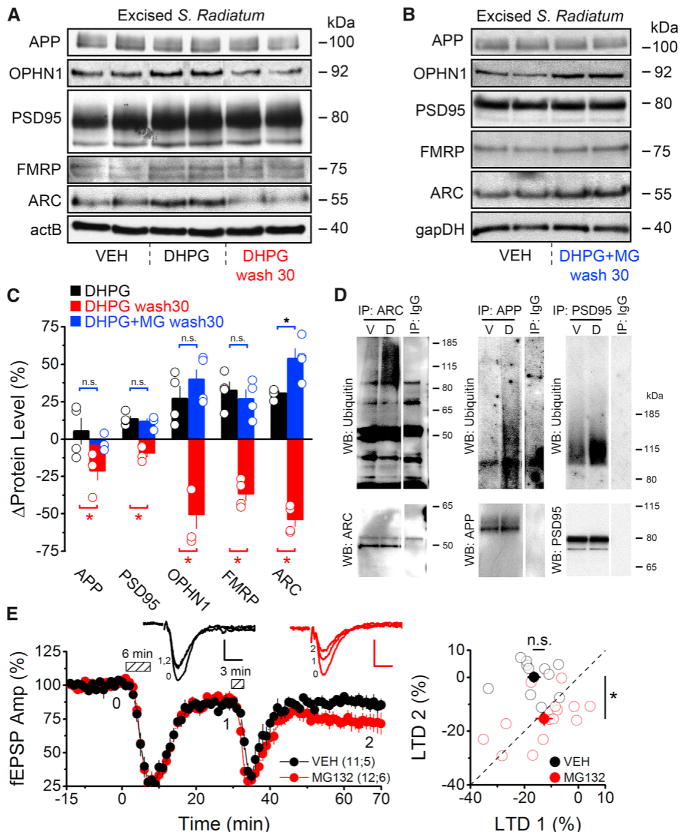
Figure 4. Proteasomal Degradation following mGluR Activation Rapidly Depletes PRPs and Inhibits Subsequent Inductions of LTD.
(A) Western blots of PRPs from rat microdissected S. Radiatum prepared immediately after DHPG treatment (100 μM, 6 min) or 30 min after DHPG washout (DHPG wash 30).
(B) Western blots of PRPs from rat microdissected S. Radiatum prepared 30 min after DHPG+MG132 washout (DHPG+MG wash 30). Slices in vehicle condition were treated with only MG132 and no DHPG.
(C) Densitometric analyses reveal DHPG application transiently increased dendritic PRP levels (DHPG) followed by a rapid depletion from peak levels 30 min after washout (DHPG wash30). PRP levels remain elevated if the proteasome was inhibited with MG132 (DHPG+MG wash30) during mGluR-LTD induction. Black bars indicate PRP levels after DHPG treatment relative to baseline conditions. Red bars indicate PRP levels 30 min after DHPG washout relative to levels immediately following DHPG treatment. Blue bars indicate PRP levels 30 min after DHPG+MG132 washout relative to control (MG132 alone).
(D) Western blots show increased ubiquitination of ARC, APP, and PSD95 after mGluR activation. Acute hippocampal slices were treated with vehicle, or DHPG (100 μM, 6 min), and lysed after 30 min of DHPG washout. Immunoprecipitations were performed as indicated, and ubiquitination was assessed by an anti-Ub Ab.
(E) (Left) Field recordings from acute hippocampal slices (rat) treated with a vehicle (VEH, black) or 5 μM MG132 (MG132, red) for 1 hr. An initial round of LTD was induced (100 μM DHPG, 6 min), followed by a subthreshold stimulus (100 μM DHPG, 3 min). Dashed boxes show time of DHPG application. (Right) For each experiment, the magnitude of the initial LTD (1) is plotted on the x axis with the magnitude of the subsequent round of LTD (2), relative to the first, plotted on the y axis. Under vehicle conditions a subthreshold stimulus did not, on average, produce a second round of LTD. However, inhibition of the proteasome allows for a subsequent round of LTD to be induced.
Summary data consist of mean ± SEM.