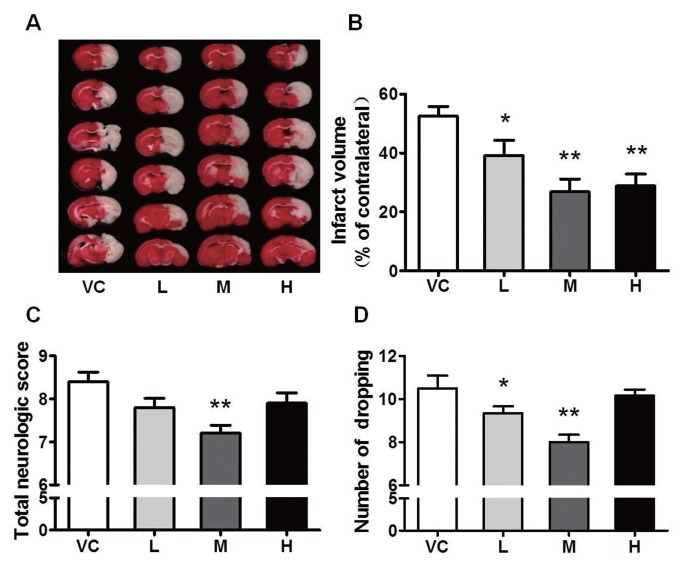
Figure 1.
MB reduces the infarct volume and improves neurological functions. (A) Representative images of TTC-stained brain sections from the vehicle- or MB-treated animals collected 24 h after infarction. VC indicates vehicle control; and L, M and H represent low (1 mg/kg), medium (5 mg/kg) and high (10 mg/kg) dose MB, respectively. (B) Quantitative analysis of the infarct volume. (C) Total neurological deficit score. The medium dose of MB significantly attenuated the injury to the impaired forelimb. (D) Grid-walking test. The number of foot faults by the animals was significantly reduced by the low or medium dose of MB. n = 18–20; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with the VC.