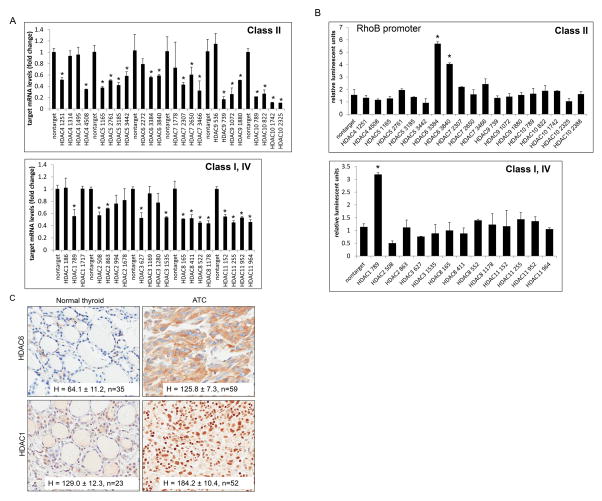
Figure 8. Identification of HDAC1 and HDAC6 as repressors of RhoB.
A. THJ-16T cells were transiently transfected with MISSION shRNA pLKO.1 constructs: nontarget, HDAC1 (clones NM_004964.2), HDAC2 (clones NM_001527.1), HDAC3 (clones NM_003883.2), HDAC4 (clones NM_006037.2), HDAC5 (clones NM_005474.3), HDAC6 (clones NM_006044.2), HDAC7 (clones NM_015401.1), HDAC8 (clones NM_018486.1), HDAC9 (clones NM_014707.1), HDAC10 (clones NM_032019.4), and HDAC11 (clones NM_024827.1). The construct clone numbers are as indicated. QPCR was performed for each set of HDACs in order to examine level of silencing. B. Luciferase RhoB reporter assay for screening transcription regulation by HDACs from class I, II and IV. THJ-16T cells were transiently transfected with renilla, RhoB-luc and verified MISSION shRNA pLKO.1 constructs as indicated. Luciferase data was normalized for transfection efficiency based upon renilla activity levels and reported as relative luminescent units ± S.D. Comparisons were analyzed by two-tailed paired Student’s t-test. *indicated, p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant as compared to nontarget control. C. IHC of patient normal and ATC tissue for HDAC1 and HDAC6 showed strong staining for both HDACs in tumor tissue as indicated by H score ± S.D. Sample size (n) was as indicated.