Fig. 4.
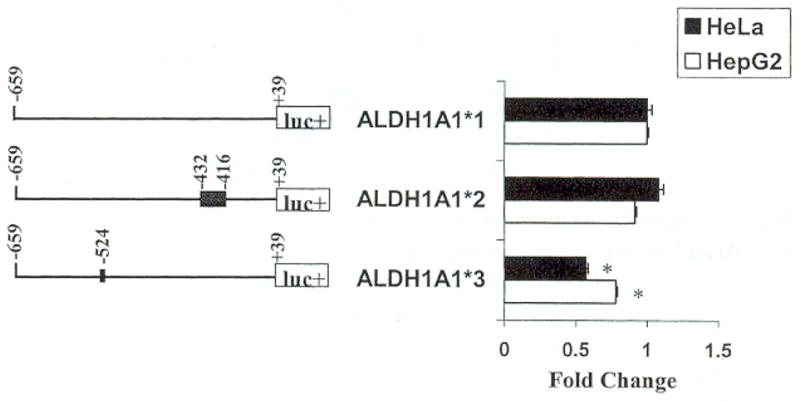
Functional importance of ALDH1A1 promoter polymorphisms. Plasmids ALDH1A1*1, ALDH1A1*2, and ALDH1A1*3 were transfected into HepG2 and HeLa cells; luc+ denotes the luciferase gene. Each respective fragment amplified from the ALDH1A1 promoter extended from −659 to +39 with respect to the transcriptional start point, and the polymorphisms, the deletion (−416/−432) and the insertion (−524), are noted. The activity of each construct was normalized by co-transfection of the internal control plasmid, pRL-CMV, and was expressed as fold change compared with the activity of ALDH1A1*1-luc. The mean ± SEM are representative of the results from three to six independent transfections performed in triplicate with two different plasmid preparations. The significance of the difference between mean values within and between multiple constructs was analyzed with ANOVA. ALDH1A1*3-luc significantly decreased luciferase expression in both Hep G2 and HeLa cells compared with ALDH1A1*1-luc (*p < 0.05). No significant change in expression was associated with ALDH1A1*2-luc.
