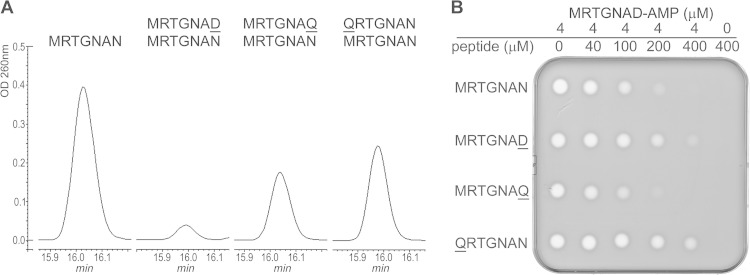
FIG 4.
Effect of MccA variants that are not subject to adenylation on wild-type MccA adenylation and on bioactivity of adenylated MccA. (A) The adenylation reaction of wild-type MccA was conducted in the presence of a 50-fold excess of QRTGNAN, MRTGNAQ, or MRTGNAD. Reaction products were separated by reverse-phase HPLC, and adenylation of wild-type MccA was determined by monitoring absorbance at 260 nm. The presence of adenylated MccA in the peak was confirmed by MALDI-MS. (B) The product of wild-type MccA adenylation was purified and combined with the indicated concentrations of MccA peptide variants, and 10-μl reaction aliquots were deposited onto cell lawns formed by E. coli cells. The results of overnight growth at 37°C are shown. The plate shown is representative of one of three independent experiments.