FIG 3.
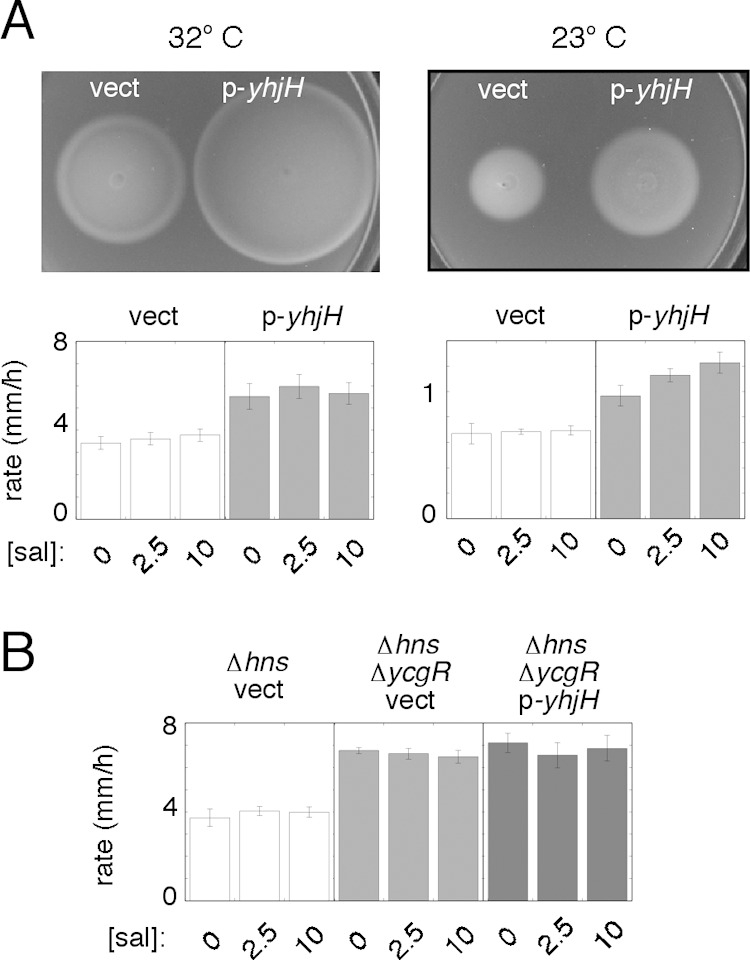
Involvement of c-di-GMP and YcgR in the motility defect of the FlhDC-constitutive Δhns mutant (strain EK2 transformed with plasmid pKP148 as a source of FlhDC and with other plasmids as indicated). (A) Effect of expression of the c-di-GMP phosphodiesterase YhjH in the mutant strain at two temperatures. Cells contained either the yhj-expressing plasmid pEK29 (p-yhjH) or the vector control pKG116 (vect), as indicated. Plates were inoculated with 3-μl spots from cultures grown overnight and incubated at 32°C (for 9 h) or 23°C (28.2 h). Plates contained 2.5 mM salicylate to induce yhjH. Induction of flhDC was done with 100 mM IPTG at 32°C or 40 μM IPTG at 23°C. Migration rates for three levels of yhjH induction are shown in the graphs at the bottom. Values are averages of data from 5 determinations (±standard errors of the means) at 32°C or 3 determinations (±standard deviations) at 23°C. (B) Motility improvement of a Δhns strain upon deletion of ycgR and lack of any additional motility rescue by expression of YhjH in the Δhns ΔycgR background. Experiments were done at 32°C. The Δhns ΔycgR strain used was MS1517; cells were transformed with plasmid pKP148 as a source of FlhDC, with induction with 100 μM IPTG. Strains expressing YhjH contained the salicylate-regulated plasmid pEK29, induced at the levels indicated; the “vect” control contained the parent vector pKG116. Values are averages of data from 3 determinations (±standard deviations).
