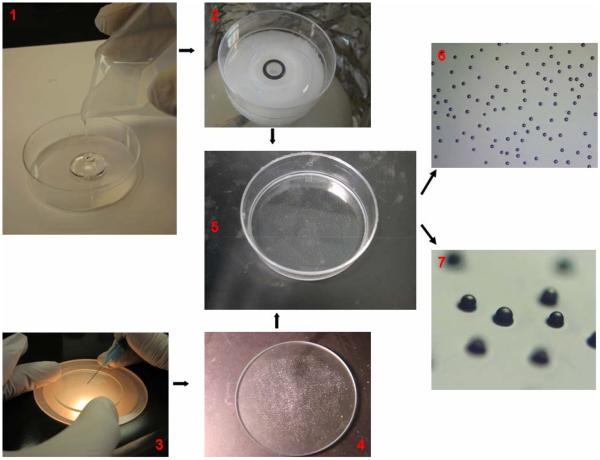
Figure 4.
Photographs illustrating how library beads are affixed on the bottom of dish. Around 1 mL PDMS solution was poured into the 60 mm cell culture dish (1). The dish was placed on the top of the rotator of spinning machine and a 5 μm thin layer of solution would form after spinning. The PDMS layer was partially cured overnight prior to bead affixation (2). A mono-layer of library beads was distributed evenly on a glass plate (50 mm in diameter) with the help of a hyperdermic needle (3). The dish was inverted and the PDMS layer on the bottom of the dish was pressed down onto the glass plate supporting the beads (4). The beads would be affixed strongly to the bottom of the dish (5) and the glass plate removed. The beads were observed from top view (10x) (6) and at an angle (40x) under the dissecting microscope (7).