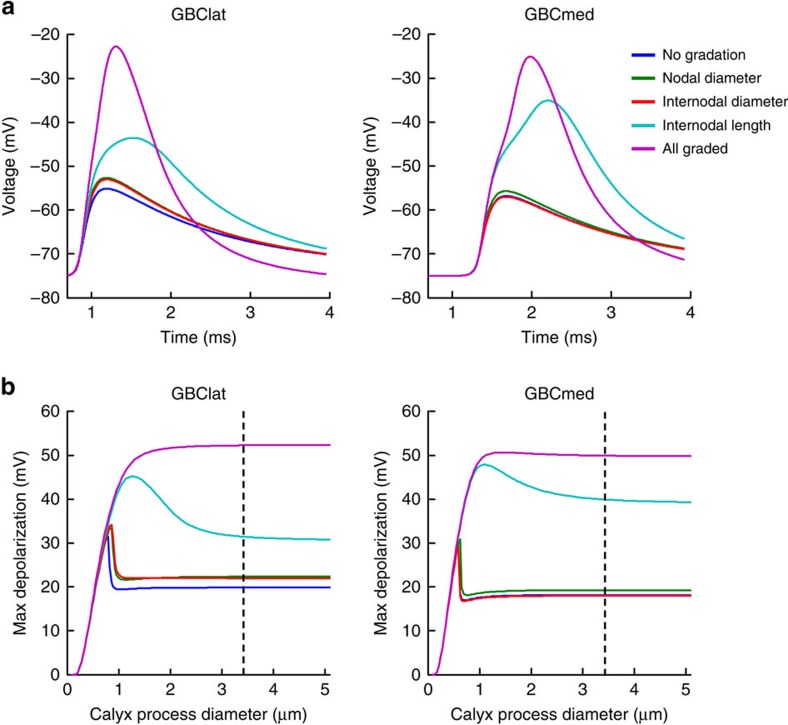
Figure 6. Computer simulations exploring the effect of morphological parameters on action potential invasion into the calyx of Held.
(a) Propagation of APs into the GBClat (left) and GBCmed (right) axon terminals is facilitated by including experimentally observed gradations of the axon and myelin parameters. The membrane potential waveform in the calyx has a shorter delay, larger amplitude and faster rate of rise when gradations of node diameter, internode diameter and internode length are included. (b) Action potential propagation into the calyx of GBClat (left) and GBCmed (right) axons occurs over a wider range of calyx geometries when experimentally observed gradations of the axon anatomy are included. When the diameter of the calyx processes was varied, while retaining the same calyx membrane surface area (thus, altering the longitudinal resistance into the calyx processes, but retaining the same conductance and capacitance across the calyx membrane), it was found that graded properties of the axon towards the end of the presynaptic axon allowed propagation of the action potential into the synaptic terminal over a wider range of calyx dimensions. Dotted line indicates calyx process diameter for which the membrane potential waveforms are shown in a. Calyx surface area was 1,700 μm2 for GBClat and 1,250 μm2 for GBCmed.