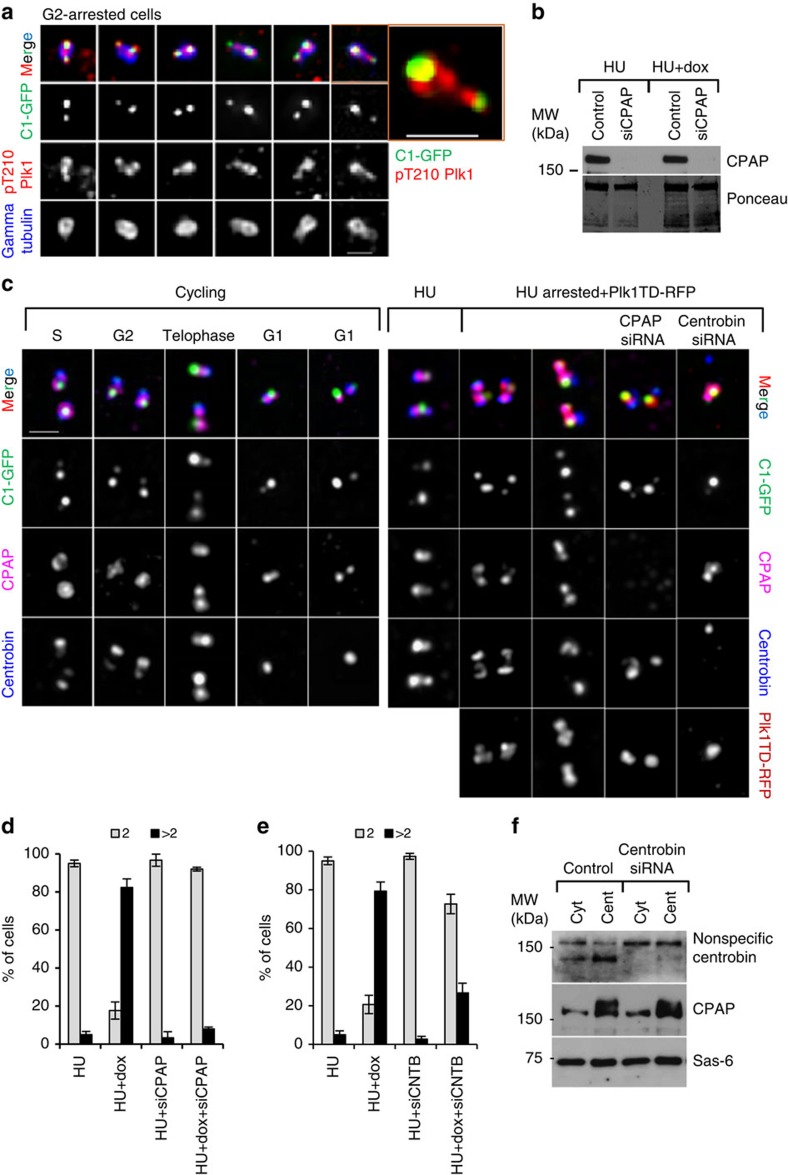
Figure 7. Depletion of CPAP prevents Plk1-dependent centriole distancing and disengagement in S-phase-arrested cells.
(a) Localization of endogenous active pT210Plk1 on the centrosomes of G2-arrested cells during centriole distancing. Plk1 signal is localized to the site of the mother centriole and along disengaging daughter centrioles. One centrosome from a is enlarged to illustrate the details. (b) Western blot analysis of total cell lysates from hydroxyurea (HU)-treated cells, to illustrate the typical level of CPAP depletion. (c) Analysis of CPAP, centrobin, Plk1TD–RFP and C1–GFP localization, under various experimental conditions. CPAP and centrobin partially co-localize within the centrosomes of cycling cells. Depletion of CPAP or centrobin prevents distancing of the daughter centrioles from the mother centrioles in HU-arrested Plk1TD-expressing cells, as judged by the proximity of their C1–GFP signals. (d,e) Quantification of individual centrosomes in the cells, judged by the number of resolvable gamma tubulin signals, after CPAP (d) and centrobin (e) depletion in HU-arrested cells expressing Plk1TD–RFP. Histograms represent the average, and the error bars the s.d. n=300, from three independent experiments. (f) Western blot analysis of cytosolic and centrosomal fractions from HU-arrested cells, after depletion of centrobin. Centrobin depletion does not change the amount of cytosolic or centrosome-associated CPAP and Sas6. Scale bars, 1 μm.