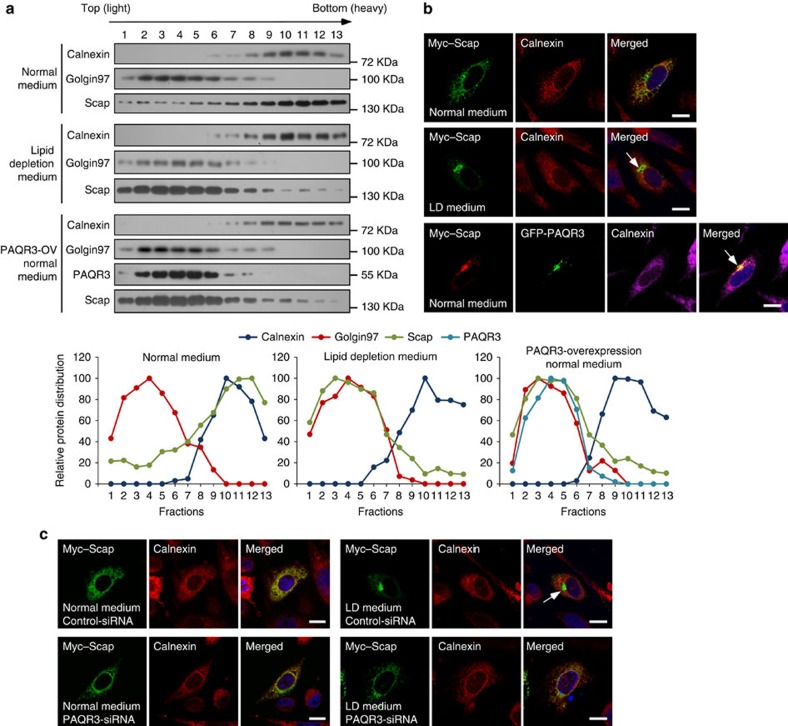
Figure 2. PAQR3 tethers Scap to the Golgi apparatus.
(a) Analysis of Scap and PAQR3 subcellular localization by fractionation. Myc-tagged Scap (for all three groups) and GFP-fused PAQR3 (for the last group) were transfected into sterol-sensitive and Scap-deficient SRD-13A cells. At 36 h after the transfection, the cells were switched to normal medium or lipid depletion medium for 90 min, and then subjected to homogenization and cell fractionation by gradient centrifugation. The relative distribution of each protein in different fractions is shown in the lower panels after densitometry analysis of the blots. (b) PAQR3 overexpression promotes Golgi localization of Scap. SRD-13A cells were transiently transfected with the plasmids as in a and used in immunofluorescence staining and confocal analysis. The arrows indicate apparent localization of Scap in the Golgi. (c) Knockdown of PAQR3 reduces lipid depletion-induced Golgi localization of Scap. SRD-13A cells were transfected either with control siRNA or PAQR3 siRNA. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were transfected with Myc-tagged Scap and cultured for 24 h. Then the cells were subjected to normal culture medium or lipid depletion medium before immunofluorescence staining and confocal analysis. The arrow indicates LD-induced localization of Scap in the Golgi. Scale bar,10 μm. All experiments were repeated at least twice with similar results and representative data are shown.