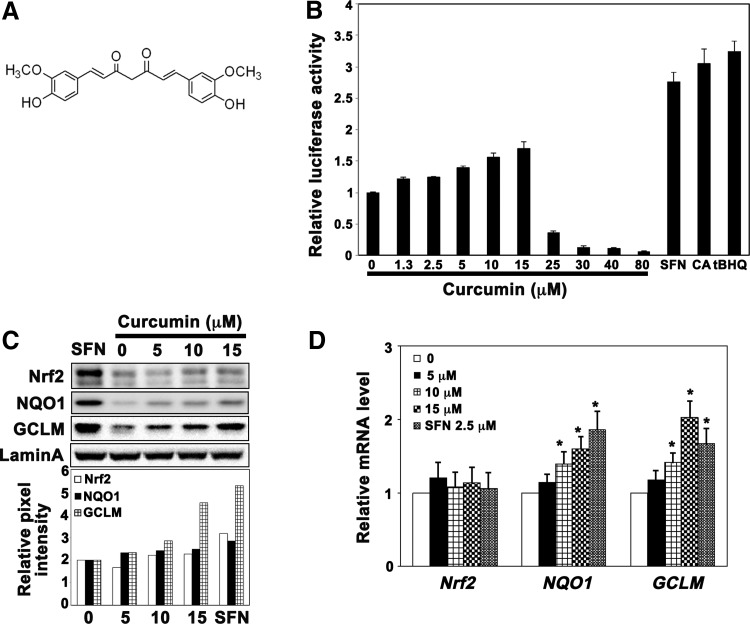
FIG. 1.
Curcumin weakly activated the Nrf2 pathway. (A) Chemical structure of curcumin. (B) Curcumin weakly induced ARE-luciferase activity. A stable MDA-MB-231 cell line expressing ARE-luciferase was treated with curcumin (0–80 μM), SFN (2.5 μM), tBHQ (25 μM), or CA (10 μM) for 16 h before luciferase activity was measured. (C) Curcumin induced the protein levels of Nrf2, GCLM, and NQO1 slightly. Total cell lysates from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with curcumin (0–15 μM) or SFN (2.5 μM) for 16 h were subjected to immunoblot analysis. (D) Curcumin enhanced the mRNA levels of NQO1 and GCLM. mRNA was extracted from MDA-MB-231 cells treated with curcumin (0–15 μM) or SFN (2.5 μM) for 16 h and subjected to quantitative qRT-PCR analysis. Results are expressed as mean±SD (n=3), *p<0.05 treated versus control. ARE, antioxidant response element; CA, cinnamaldehyde; GCLM, glutamate-cysteine ligase, modifier subunit; NQO1, NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction; SD, standard deviation; SFN, sulforaphane; tBHQ, tert-butylhydroquinone.