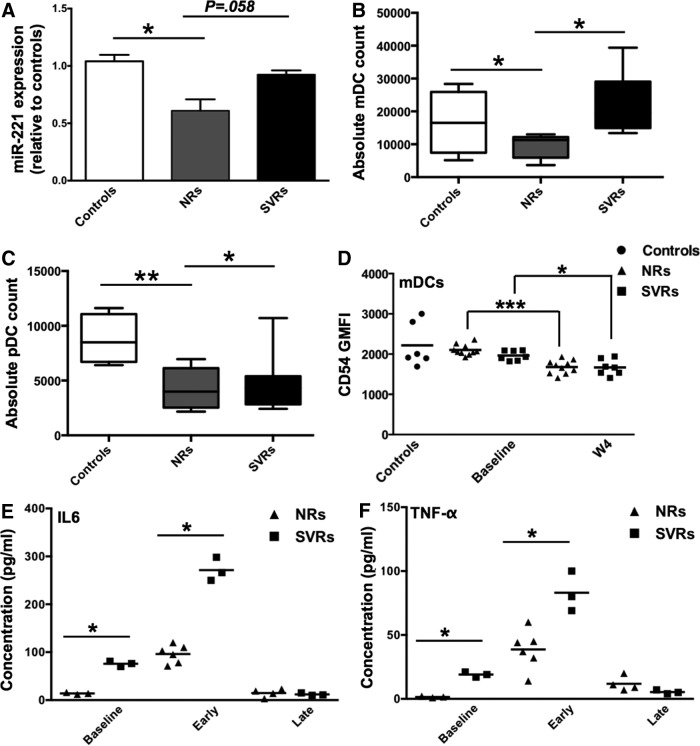
FIG. 6.
Role of miR-221 in IFN/Ribavirin treatment response against HCV. (A) Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMCs) were isolated from seronegative controls (n=6) and non-responders (NRs) (n=10) and sustained virological responders (SVRs) (n=7) at week 0 (baseline) of IFN/Ribavirin treatment. Bar graph indicates mean fold change in miR-221 levels in NRs (gray bar) and SVRs (black bar) relative to seronegative controls (white bar). P values were calculated using Student's t test (*P<0.05). Error bars represent standard deviation. (B) Box and Whiskers plot indicating mDC count in seronegative controls, NRs and SVRs (C) Box and Whiskers plot indicating pDC count in seronegative controls, NRs and SVRs (D) PBMCs from seronegative controls, NRs and SVRs were stained with polychromatic flow cytometry Ab cocktail consisting of Lin-1, CD11c, CD123, and CD54 Abs. Lin-1 was used to gate on DCs and CD11c and CD123 were used to gate on mDCs (CD11c+ CD123−). Scatter plot indicates CD54 GMFI in controls, NRs, and SVRs at week 0 and week 4 of treatment. (E) PBMCs isolated from NRs and SVRs at week 0 (baseline), early weeks (within first 4 weeks) and last weeks (last 4 weeks) of treatment were stimulated in vitro with IFN-α-2a/Ribavirin for 24 h, and concentrations of a panel of 12 Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokines were determined in culture supernatant using ELISA. Scatter plot indicates the concentration of IL-6, and (F) TNF-α in NRs and SVRs. P values were calculated using Mann–Whitney's test (*P<0.05; **P<0.01). Horizontal bars represent mean concentration.