Fig. 2.
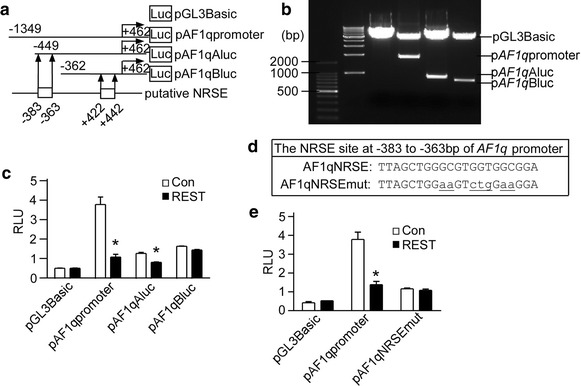
Identification of the functional NRSE site in AF1q gene promoter. a Schematic diagrams of the AF1q promoter deletion constructs consisting of a 5′-flanking region with serial deletions cloned into the promoter-less vector plasmid pGL3-Basic in front of the luciferase reporter gene. Arrow indicated the direction of transcription. The numbers represented the end points of each construct. The positions of two putative NRSE sites were shown at the bottom. b The deletion plasmids were confirmed by sequencing and restriction enzyme digestion on a 1.5 % agarose gel. Vector size is 4.7 kb, and the AF1q gene 5′-flanking fragment inserts ranged from 0.6 to 1.8 kb. c HEK293 cells were co-transfected with REST expression vector and various AF1q promoter deletion constructs. Plasmid pRL-TK was used to normalize the transfection efficiency, and luciferase activity was measured at 24 h by a luminometer. The values represented the mean ± SE (n = 3). *P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. d pAF1qNRSEmut was made to contain the mutant NRSE site at −383 to −363 of p AF1qAluc, where (5′-TTAGCTGGGCGTGGTGGCGGA-3′) was mutated to (5′-TTAGCTGGaaGTctgGaaGGA-3′). e HEK293 cells were co-transfected with REST expression vector and AF1q promoter or pAF1qNRSEmut. Plasmid pRL-TK was used to normalize the transfection efficiency, and luciferase activity was measured at 24 h by a luminometer. The values represented the mean ± SE (n = 3). *P < 0.01 by Student’s t test
