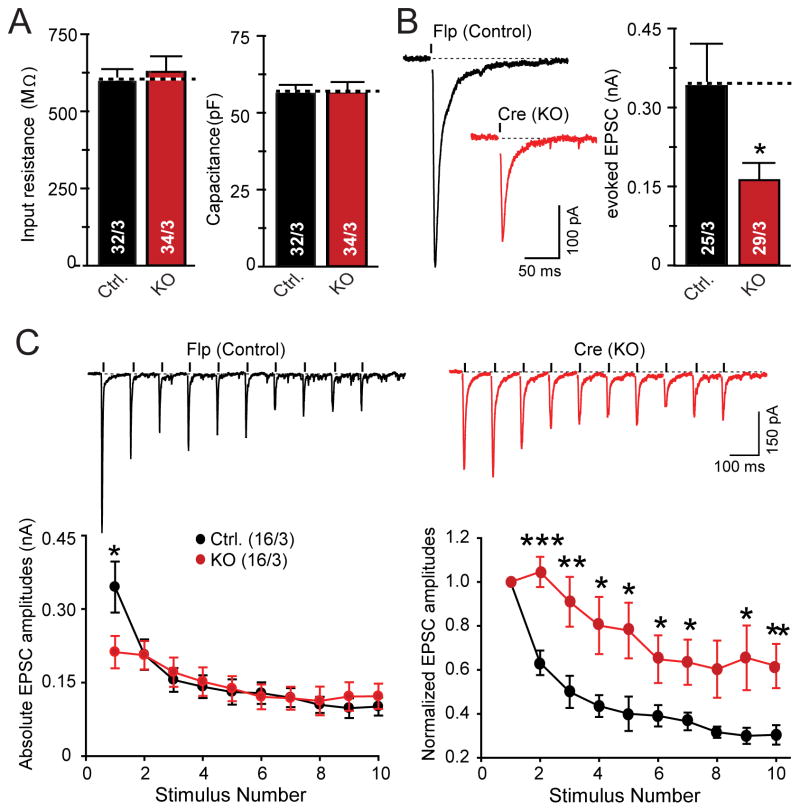
Figure 6. Heterozygous NRXN1 cKO impairs evoked excitatory synaptic responses in human neurons derived by a standard differentiation protocol.
All data are from human neurons generated from NRXN1 cKO ES cells as shown in Fig. 5A, with lentiviral expression of Flp- or Cre-recombinases at day 20.
(A) Input resistance and capacitance values are identical in control and NRXN1 cKO neurons.
(B) ESPCs evoked by isolated action potentials exhibit a ~2-fold decrease in amplitude in NRXN1 cKO neurons (left, representative traces; right, summary graphs).
(C) EPSCs evoked by a 10 Hz stimulus train exhibit a decreased initial amplitude, but subsequent normal amplitudes in NRXN1 cKO neurons (top, representative traces; bottom left, summary plot of absolute EPSC amplitudes; bottom right, summary plot of normalized amplitudes to illustrate the apparent decrease in synaptic depression).
Data are means ± SEM; numbers in graphs represent number of total cells/independent cultures analyzed. Statistical analyses were performed by Student’s t-test (A,B) or the Mann-Whitney rank sum t-test (C) comparing test samples to control (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).