Figure 2. Functional characteristics of ACM-derived CD11b+Gr1+ cells.
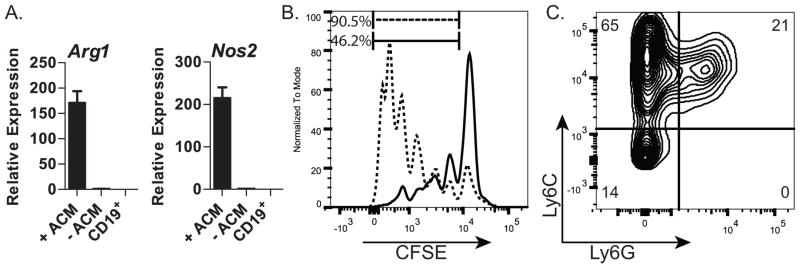
(A) qRT-PCR analysis of Arg1 and Nos2 in sorted CD11b+Gr1+ cells from cultures treated with (+ACM) or untreated (-ACM). CD19+ cells were used as a negative control; (B) Flow cytometric profile of activated, CSFE-labeled CD4+ splenocytes cultured in the presence of ACM-generated CD11bhiGr1+ cells (—) or control cells (CD19+) (- - -); (C) Flow cytometric analysis of CD11b+ cells resulting from ACM-treated cultures for expression of Ly6C and Ly6G; Data in A are representative of two independent experiments. Data in B&C are representative of three independent experiments. Error bars show the average of triplicate wells ± SD.
