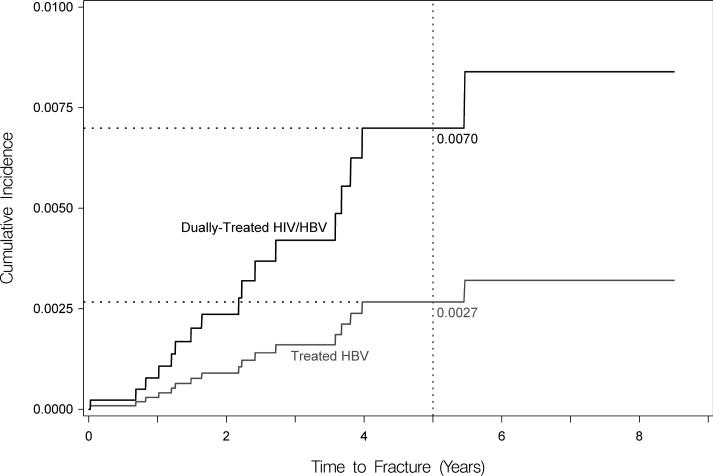
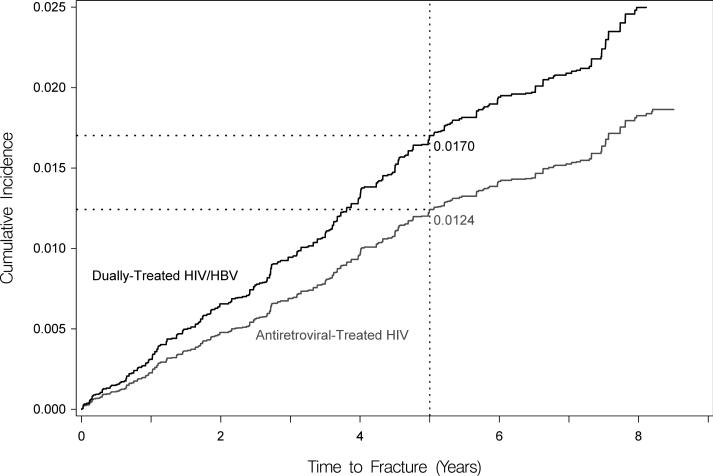
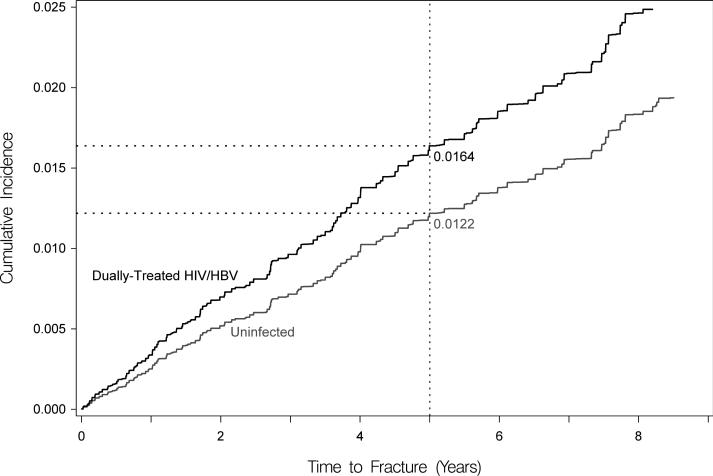
Figure 2. Standardized cumulative incidences (i.e., risks) of hip fracture, based on competing risk regression analyses.
Estimates of the cumulative incidence of hip fracture are reported for each group. Estimates are standardized to the characteristics of dually-treated HIV/hepatitis B virus coinfected patients.
(A) Standardized cumulative incidences (i.e., risks) of hip fracture between dually-treated HIV/hepatitis B virus-coinfected (denoted by black line) and treated hepatitis B virus-monoinfected patients (denoted by gray line). Coinfected patients in this figure represent only a subset of all coinfected patients. Remaining coinfected patients could not be matched to the hepatitis B virus-monoinfected patients because the characteristics of the two groups differed so markedly. Standardized for age and sex after matching.
(B) Standardized cumulative incidences (i.e., risks) of hip fracture between dually-treated HIV/hepatitis B virus-coinfected (denoted by black line) and antiretroviral-treated HIV-monoinfected patients (denoted by gray line). Standardized using age, sex, and tenofovir use after matching.
(C) Standardized cumulative incidences (i.e., risks) of hip fracture between dually-treated HIV/hepatitis B virus-coinfected (denoted by black line) and HIV/hepatitis B virus-uninfected patients (denoted by gray line). Standardized for age and sex after matching.