Figure 5.
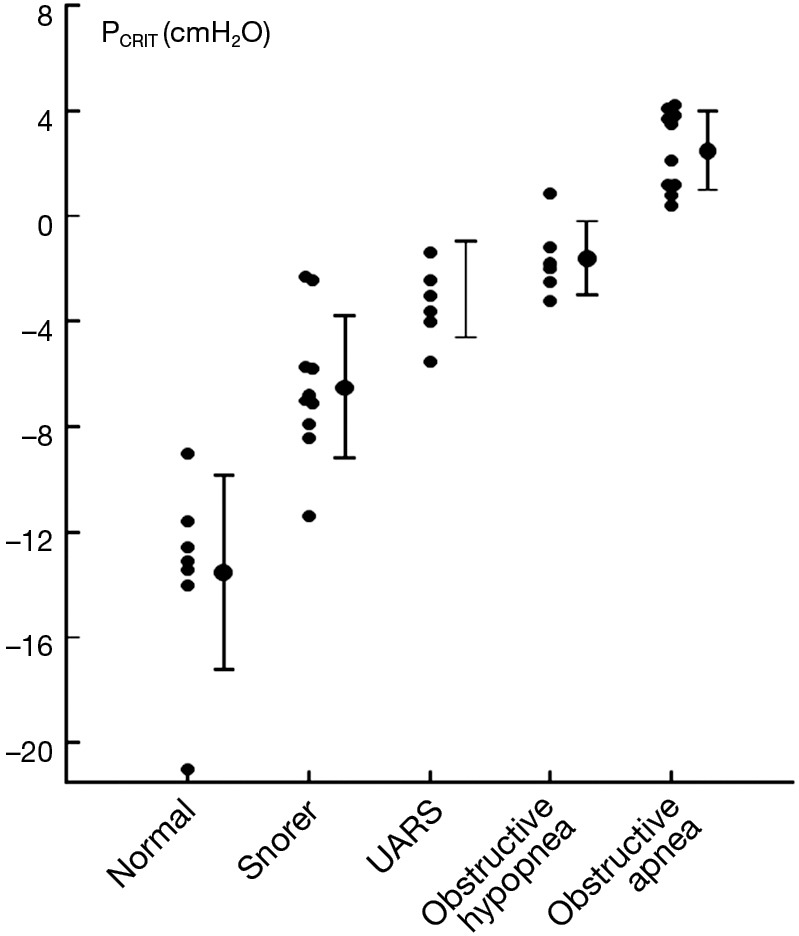
Relationship between PCRIT and clinical disorders characterized by upper airway obstruction during sleep. As PCRIT increases, the severity of upper airway obstruction also increases progressively, suggesting a dose-response relationship between upper airway collapsibility and worsening obstruction in asymptomatic snorers and patients with upper airway resistance syndrome (UARS), obstructive hypopneas, and obstructive apneas. Adapted from Schwartz et al. 1988 and Gleadhill et al. 1991 (25,27).
