Figure 8.
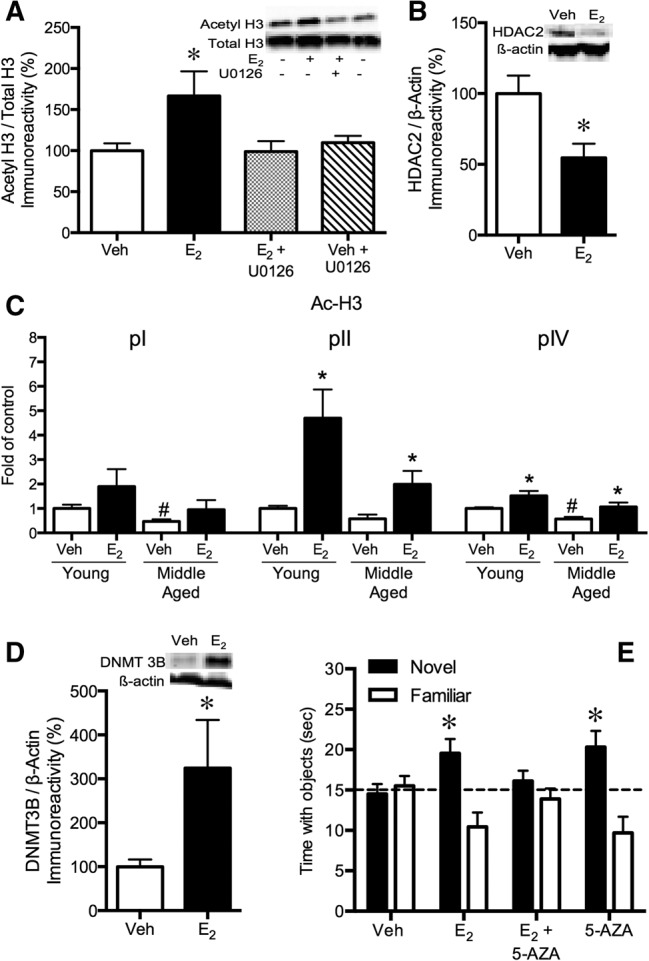
Histone acetylation and DNA methylation are critical for E2 to enhance object recognition memory consolidation in ovariectomized mice. (A) Dorsal hippocampal infusion of 5 μg/hemisphere E2 significantly increased acetyl H3 protein levels in the dorsal hippocampus within 30 min (*P < 0.05 relative to vehicle). This increase was blocked by the ERK activation inhibitor U0126, suggesting that the E2-induced increase in H3 acetylation is dependent on ERK phosphorylation. (Adapted from Zhao et al. 2012.) (B) Dorsal hippocampal infusion of 5 μg/hemisphere E2 significantly decreased HDAC2 protein levels in the dorsal hippocampus within 4 h relative to vehicle (*P < 0.05). (Adapted from Zhao et al. 2012.) (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis showed that dorsal hippocampal E2 infusion increased acetylation of Bdnf promoters pII and pIV in both young and middle-aged ovariectomized mice (*P < 0.05 relative to age-matched controls). Among vehicle-infused controls, acetylation of pI and pIV was significantly lower in middle-aged females than in young females (#P < 0.05 relative to young vehicle-infused controls), indicating an age-related reduction in acetylation of these promoters. Data were normalized to LINE1 for each sample and then normalized to young vehicle-infused mice for each promoter region and represented as fold of control. (D) Dorsal hippocampal infusion of 5 μg/hemisphere E2 significantly increased DNMT3B protein levels in the dorsal hippocampus of young ovariectomized mice within 4 h relative to vehicle (*P < 0.05). (Adapted from Zhao et al. 2010.) (E) Dorsal hippocampal infusion of 5-AZA prevented E2 from enhancing object recognition memory consolidation. E2 or 5-AZA alone enhanced memory consolidation (*P < 0.05 relative to chance). (Adapted from Zhao et al. 2010.) For all panels, each bar represents the mean ± SEM. Acetyl H3 was normalized to total H3. HDAC2 and DNMT3B were normalized to β-actin. Insets are representative Western blots of phosphorylated and total protein.
