Figure 3.
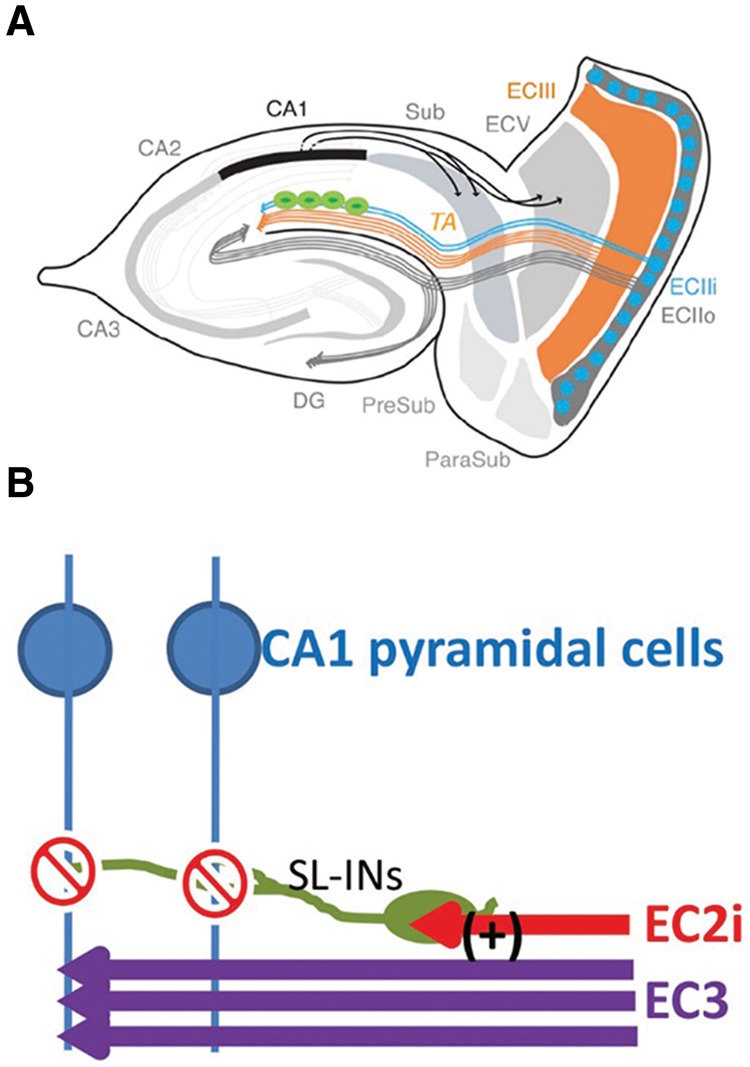
Island cells gate the MECIII input into the CA1 pyramidal cells through the feedforward inhibition. (A) New diagram of entorhinal hippocampal circuits. Pyramidal Island cells (blue, ECIIi) directly project to stratum lacunosum (SL) of CA1 region to synapse with the GABAergic interneurons (green) in SL (SL-INs). (B) Strategic location of SL-INs and projections from MECIII and Island cells. Island cells axons innervate the stratum lacunosum (SL), whereas MECIII cells axons innervate the stratum moleculare (SM) immediately adjacent to the SL. This strategic location of SL-INs (green), the primary target of Island cells, immediately adjacent to the inner side of the SM layer where MECIII cells synapse to the distal dendrites of CA1 pyramidal cells (blue) enables Island cells (Morrissey et al. 2012) to suppress MECIII input (purple) by feedforward inhibition.
