Figure 4.
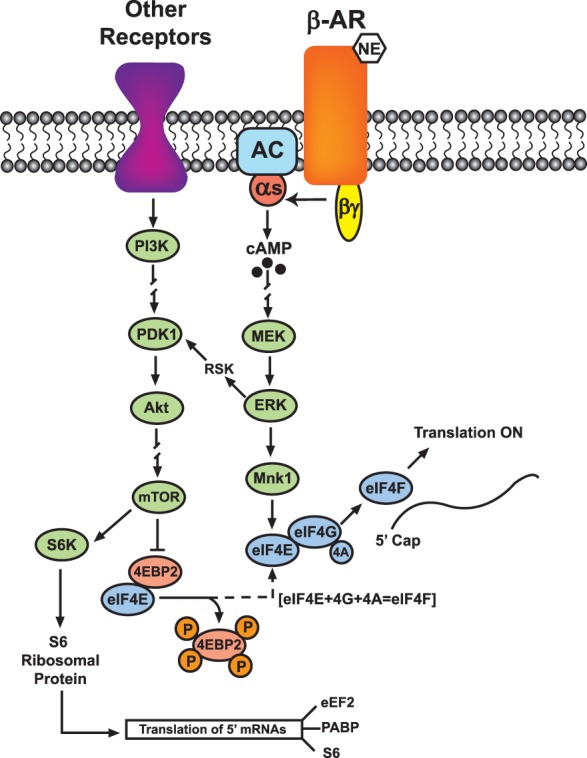
Translational control by ERK and mTOR. Activation of β-ARs during synaptic stimulation promotes translation initiation through ERK and mTOR pathways. mTOR phosphorylates and inhibits 4E-BP2 (4E-binding protein 2), releasing eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) from repression by 4E-BP2. eIF4E assists translation initiation by binding to eIF4G to form the initiation complex eIF4F. mTOR also activates S6 kinase (S6K), which phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6 to increase synthesis of translation regulatory proteins such as eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2), poly(A) binding protein (PABP), and S6 itself. ERK may cross-talk with the mTOR pathway via ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK), phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1 (PDK1), and protein kinase-B (Akt). Diagram is simplified.
