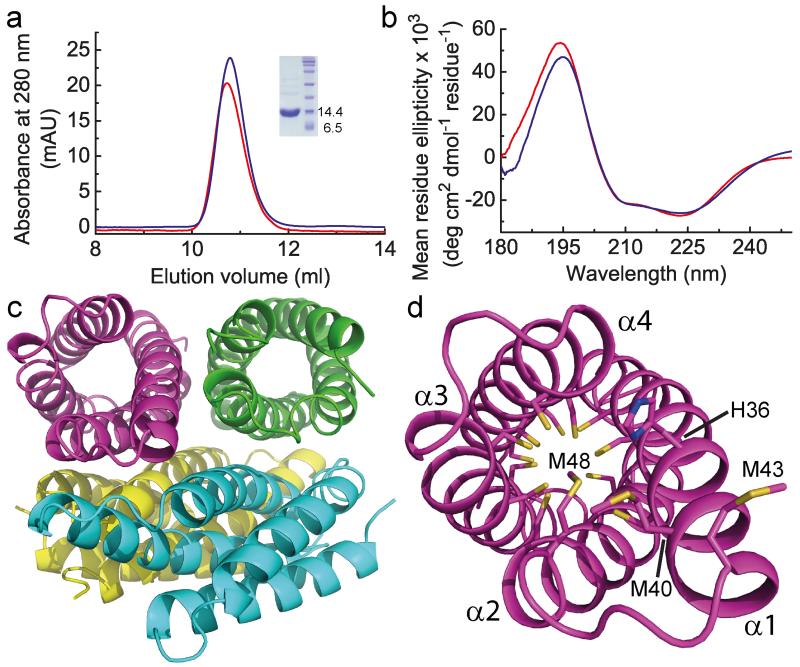
Figure 2. The structure of apo-Csp1.
a, Analytical gel-filtration chromatograms of apo-Csp1 (red line) and protein to which 14.0 molar equivalents of Cu(I) were added (blue line) for samples (100 μM when injected) in 20 mM 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid (Hepes) pH 7.5 containing 200 mM NaCl. The absorbance was monitored at 280 nm with the values for Cu(I)-Csp1 divided by 10 (see Extended Data Fig. 2a, b). The inset shows SDS-PAGE analysis of the purified protein. b, Far-UV CD spectra of apo-Csp1 (red line) and Csp1 plus 14.0 equivalents of Cu(I) (blue line) at 39.6 and 35.7 μM respectively in 100 mM phosphate pH 8.0. c, The tetrameric arrangement in the asymmetric unit of the crystal structure of apo-Csp1, with the side-chains of the Cys residues that point into the core of the 4-helix bundle shown as sticks for one monomer in (d). The opening into the core of the 4-helix bundle is facing out in (d), and involves His36, Met40, Met43 (on the extended α1) and Met48.