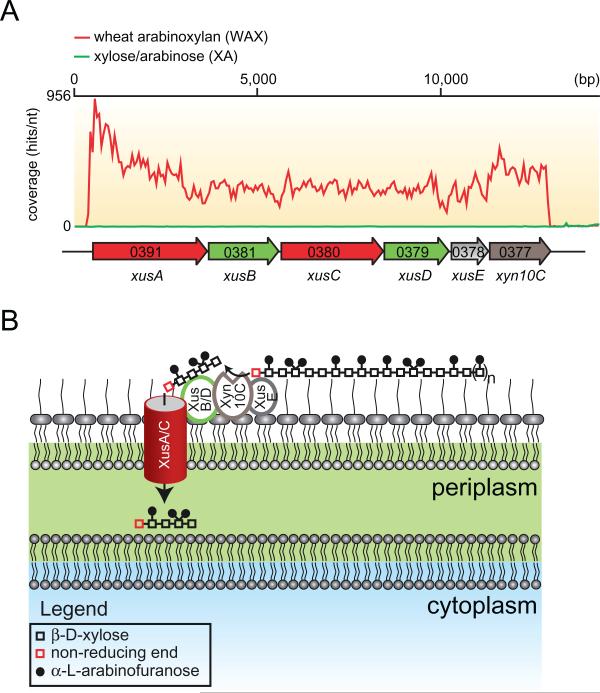
Fig. 2.
Model for the xylan utilization system in xylanolytic Bacteroidetes.
A. RNAseq coverage map of the major xylan utilization system in P. bryantii B14 during growth on soluble wheat arabinoxylan (WAX, red line) or a mixture of xylose and arabinose (XA, green line). Total RNA was extracted from P. bryantii B14 cultured on either growth substrate (WAX or XA), and then rRNA was subtracted and the enriched mRNA was converted to cDNA. The cDNA was directly sequenced by Illumina technology and individual sequence reads were assembled onto the genome sequence of P. bryantii B14. These data are derived from Dodd et al. (2010a).
B. Predicted model for binding of xylan, cleavage and transport of xylan fragments across the outer membrane by components of the Xus cluster in P. bryantii B14. The proteins, XusA and XusC, are homologues of the SusC TonB-dependent receptor, which is involved in oligosaccharide transport across the outer membrane in B. thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482. XusB and XusD are homologues of B. thetaiotaomicron VPI-5482 SusD, which binds polysaccharides on the outer leaflet of the outer membrane. XusE has no homology to other characterized proteins, but the presence of an N-terminal signal peptidase II cleavage site in this protein suggests that it is tethered to the outer leaflet of the outermembrane. Xyn10C is an endoxylanase gene that also possesses a putative N-terminal signal peptidase cleavage II site. In the predicted model, XusE, Xyn10C and the XusB/D proteins bind to extracellular xylan polymers. Xyn10C then catalyses the endo-cleavage of these polymers and XusB/D facilitate transport of these fragments across the outer membrane and into the periplasm through the TonB-dependent receptors XusA and XusC.