Figure 9.
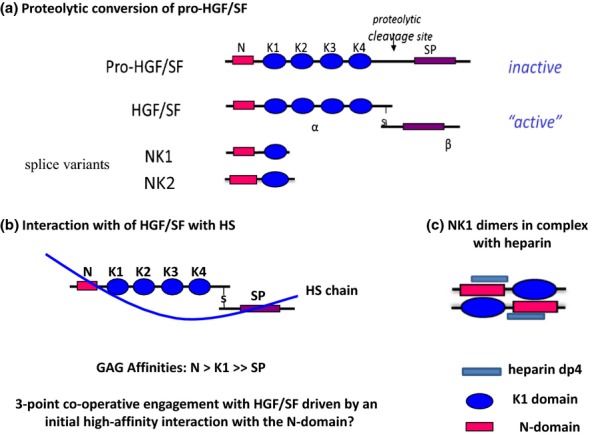
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF), its splice variants and interactions with heparan sulphate (HS). (a) HGF/SF is a disulphide-linked heterodimer with an N-terminal hairpin loop (N), four kringle domains (K1–K4) and an inactive serine protease (SP) domain. The primary HS-binding site is in the hairpin loop, with accessory sites in the K1 and SP regions. NK1 and NK2 are splice variants of the hgf/sf gene. (b) HS S domains of length dp12-dp14 are the optimum size for high-affinity binding to HGF/SF. In principle, HS fragments of this length are sufficient to engage in a three-point attachment to HGF/SF that may stabilize an active conformation of the modular elements in the native protein. (c) NK1 has an absolute requirement for HS or heparin to bind the Met receptor and for signalling activity in cultured cells. In crystal structures, NK1 forms dimers in the presence of heparin and four sulphated monosaccharides make contact with the binding site in the N-domain. Heparin (or HS) may stabilize the dimer and/or expose the dimerization surfaces in the N and K1 regions. The tendency for NK1 domains to form stable interactions in the presence of heparin suggests a mechanism for dimerization and activation of native HGF/SF.
